末梢静脈カテーテル
末梢静脈カテーテル (まっしょうじょうみゃくカテーテルまたは末梢血管内カテーテル、英: peripheral venous catheter)[1] は、医療において、薬剤や輸液、輸血などの静脈内注射を行うために末梢静脈に入れるカテーテル (細い柔軟な管) である。静脈留置針 (じょうみゃくりゅうちしん) または単に留置針と呼ばれる事も多い。︵末梢︶静脈ラインと呼ばれることもあるが、この場合はカテーテルだけではなく、それに接続される点滴セットをも含むことがある。
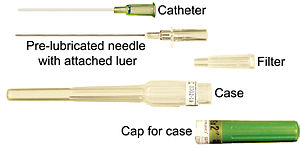


使用法
編集
カテーテルは、採血と同じように針で静脈に挿入され、その後、小さなプラスチック製のカニューレはそのままに、針は抜かれる。その後、カテーテルを患者の皮膚にテープ固定するか、粘着性のある創傷被覆材(ドレッシング) を使用して固定する。
末梢静脈カテーテルは、医療現場で最もよく使用される血管アクセスである。救急外来や外科の患者のほとんどに、また、放射線造影剤を使用する一部の放射線画像診断の前などにも投与される。米国では、1990年代には、毎年2,500万人以上の患者に末梢静脈ラインが留置されていた[2]。
末梢静脈カテーテルは、通常、手または腕の静脈に挿入される。中心静脈 (通常、首の内頸静脈または胸の鎖骨下静脈) に挿入する中心静脈カテーテルと区別する必要がある。小児などでは、痛みを和らげて挿入を容易にするために、局所麻酔薬 (リドカインなど) のテープ剤を挿入部位に貼付することがある[3]。
末梢静脈カテーテル挿入時、または留置後に採血も可能である[4]。このカテーテルは血圧測定や採血のために動脈に留置されることもある[5]。
詳細は「動脈ライン」を参照
-
末梢静脈カテーテルの持ち方の一例。ハブの端は点滴に繋ぐので不潔にならないように触れていない。
-
末梢静脈カテーテルの外筒の進め方の一例。内筒は鋭利だが、外套はプラスチック製であり、外筒を内筒より先進させると血管内壁を傷つけにくくなる。
合併症
編集
感染、静脈炎、点滴漏れ、空気塞栓症、出血、血腫形成 (いわゆる青あざ) などが起こることがある。カテーテル塞栓症は、カニューレの一部が切れて血管内に流れ込むことで発生し得る。末梢静脈カニューレを抜去する際には、先端が無傷であることを確認する必要がある[7]。
挿入部位感染のリスクを理由として、アメリカ疾病予防管理センター(CDC)はガイドラインでカテーテルを96時間ごとに交換する必要があると勧告している[8]。しかし、これらのカテーテルを日常的に交換する必要性については議論もある[9]。 専門家が管理すれば、末梢ラインの合併症は減ることが示されている[2][10]。カテーテルの不具合の低減に関して、どのドレッシング (創傷被覆材) や固定具が他より優れているかは結論が出ていない[11]。
サイズ
編集末梢静脈カテーテルのサイズは、ゲージ又はフレンチスケールで表される。針の直径はフレンチスケールに比例し、ゲージに反比例する。
| ゲージ | 直径 (mm) | 点滴時の最大流速 (ml/分)[12] |
色[12] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 26 | 0.46 | 13-15 | Black |
| 24 | 0.60 | 36 | Yellow |
| 22 | 0.90 | 56 | Blue |
| 20 | 1.10 | 40-80 | Pink |
| 18 | 1.30 | 75-120 | Green |
| 17 | 1.50 | 128-133 | White |
| 16 | 1.80 | 236 | Grey |
| 14 | 2.00 | 270 | Orange |
歴史
編集
プラスチック製のカニューレを挿入し、針を引き抜く方法は、1945年に技術導入された[13]。最初に販売された使い捨てタイプは、1964年に販売された﹁アンジオキャス﹂である。1970年代から1980年代にかけて、プラスチック製カニューレの使用が日常化し、その挿入は看護スタッフに委ねられることが多くなった[14]。
最近のカテーテルには、針刺し事故を避けるための安全機能が追加されている。現代のカテーテルは、テフロンなどの合成ポリマーで製造されている (そのため、これらの静脈カテーテルには﹁ベンフロン﹂または﹁キャスロン﹂などという用語がよく使用される)。1950年は、ポリ塩化ビニル製であった[15][16]。1983年には、ポリウレタン製のものが初めて登場した[14]。
補足画像
編集-
-
カテーテル留置直前
-
使用していないときのカテーテル
-
安全機構つきの新型カテーテル
脚注
編集注釈
編集出典
編集
(一)^ “Management of Peripheral Intravenous Catheters Clinical Care Standard | Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care”. www.safetyandquality.gov.au. Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. 2023年1月11日閲覧。
(二)^ ab“Prevention of peripheral venous catheter complications with an intravenous therapy team: a randomized controlled trial”. Arch. Intern. Med. 158 (5): 473–77. (March 1998). doi:10.1001/archinte.158.5.473. PMID 9508225.
(三)^ “ペンレステープ18mg”. www.info.pmda.go.jp. 2023年1月11日閲覧。
(四)^ Lesser, Finnian D; Lanham, David A; Davis, Daniel (6 May 2020). “Blood sampled from existing peripheral IV cannulae yields results equivalent to venepuncture: a systematic review”. JRSM Open 11(5): 205427041989481. doi:10.1177/2054270419894817. PMC 7236571. PMID 32523703.
(五)^ “橈骨動脈カテーテル挿入 - 21. 救命医療”. MSDマニュアル プロフェッショナル版. 2024年5月26日閲覧。
(六)^ Weegenaar (2018年8月21日). “Pneumothorax | Acute Management” (英語). Geeky Medics. 2020年1月14日閲覧。
(七)^ Doyle, Glynda Rees; McCutcheon, Jodie Anita (2015-11-23). “8.2 Intravenous Fluid Therapy” (英語). Clinical Procedures for Safer Patient Care
(八)^ CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report Aug 2002. “Guidelines for the Prevention of Intravascular Catheter-Related Infections”. 2008年3月13日閲覧。
(九)^ “Is routine replacement of peripheral intravenous catheters necessary?”. Arch. Intern. Med. 158 (2): 151–56. (January 1998). doi:10.1001/archinte.158.2.151. PMID 9448553.
(十)^ “Reduction in nosocomial intravenous device-related bacteremias after institution of an intravenous therapy team”. J Intraven Nurs 19(2): 103–06. (1996). PMID 8852171.
(11)^ Marsh, Nicole; Webster, Joan; Mihala, Gabor; Rickard, Claire M (2015-06-12). “Devices and dressings to secure peripheral venous catheters to prevent complications” (英語). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (6): CD011070. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011070.pub2. PMID 26068958.
(12)^ abp. 110 in: Edward Doyle (2007). Paediatric Anaesthesia. OUP Oxford. ISBN 9780199202799
(13)^ Narr, Bradly J.; Southorn, Peter A. (1 October 2008). “The Massa or Rochester Plastic Needle” (英語). Mayo Clinic Proceedings 83(10): 1165–1167. doi:10.4065/83.10.1165. ISSN 0025-6196. PMID 18828978 2019年4月16日閲覧。.
(14)^ ab“The history of peripheral intravenous catheters : How little plastic tubes revolutionized medicine”. Acta Anaesthesiol. Belg. 56(3): 271–82. (2005). PMID 16265830.
(15)^ Massa DJ; Lundy JS; Faulconer A, Jr; Ridley RW (5 Jul 1950). “A plastic needle.”. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin 25(14): 413–15. PMID 15430460.
(16)^ “Peripheral intravenous catheter use in Europe: Towards the use of safety devices”. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 52(6): 798–804. (August 2008). doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.2008.01664.x. PMID 18477072.
(17)^ p. 349 in: James R. Roberts, Jerris R. Hedges (2013). Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine E-Book (6 ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 9781455748594
関連項目
編集外部リンク
編集- アメリカ国立がん研究所 末梢静脈カテーテルについて at the Wayback Machine (archived 2008-10-01)
- 末梢静脈カテーテルの挿入と管理に関する推奨事項 クイーンズランド州政府 at the Wayback Machine (archived 2012-04-27)