This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (June 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message)
|
The tympanic ductorscala tympani is one of the perilymph-filled cavities in the inner ear of humans. It is separated from the cochlear duct by the basilar membrane, and it extends from the round window to the helicotrema, where it continues as vestibular duct.
| Tympanic duct | |
|---|---|
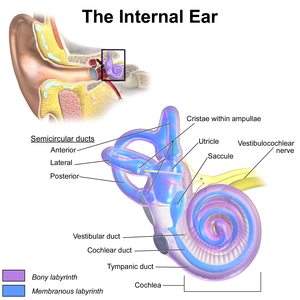
Inner ear, with tympanic duct labeled near bottom.
| |

Cross section of the cochlea (scala tympani labeled at bottom)
| |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | scala tympani |
| MeSH | D012533 |
| TA98 | A15.3.03.045 |
| TA2 | 6970 |
| FMA | 61272 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The purpose of the perilymph-filled tympanic duct and vestibular duct is to transduce the movement of air that causes the tympanic membrane and the ossicles to vibrate, to movement of liquid and the basilar membrane. This movement is conveyed to the organ of Corti inside the cochlear duct, composed of hair cells attached to the basilar membrane and their stereocilia embedded in the tectorial membrane. The movement of the basilar membrane compared to the tectorial membrane causes the stereocilia to bend. They then depolarise and send impulses to the brain via the cochlear nerve. This produces the sensation of sound.
This gallery of anatomic features needs cleanup to abide by the medical manual of style. Galleries containing indiscriminate images of the article subject are discouraged; please improve or remove the gallery accordingly. (June 2015)
|
This anatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |