Calcium diglutamate, sometimes abbreviated CDG and also called calcium biglutamate, is a compound with formula Ca(C5H8NO4)2. It is a calcium acid saltofglutamic acid. CDG is a flavor enhancer (E number E623)—it is the calcium analog of monosodium glutamate (MSG). Because the glutamate is the actual flavor-enhancer, CDG has the same flavor-enhancing properties as MSG but without the increased sodium content.[1] Notably, only the L isomer is used in flavouring as D-glutamate does not have an umami/savoury flavour.[2][3]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
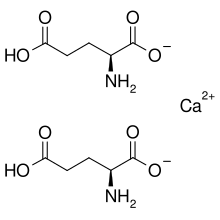
| IUPAC name
Calcium bis[(2S)- 2-amino-4-carboxy-butyrate] | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | CDG, CBG |
| 11158966 | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.025.307 |
| E number | E623 (flavour enhancer) |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H16CaN2O8 | |
| Molar mass | 332.322 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
As a soluble source of calcium ions, this chemical is also used as a first-aid treatment for exposure to hydrofluoric acid.[4]
Calcium di-glutamate can be prepared by reacting calcium carbonate with two molar equivalents of glutamic acid:[5]
Concentration of the solution to a syrup under reduced pressure, followed by gradual crystallisation, affords the monohydrate.[5] Structurally, the glutamate anion is zwitterionic, with the amino group protonated (pKa = 9.47) and both carboxylic-acid groups (pKa = 2.10, 4.07) in their deprotonated carboxylate form.[6]
Calcium di-L-glutamate can be used to prepare other glutamates through metathesis with a soluble sulfate, carbonate or hydroxide salt. For example, manganese(II) di-L-glutamate can be prepared through metathesis with manganese(II) sulphate:[7]