

Anillegal number is a number that represents information which is illegal to possess, utter, propagate, or otherwise transmit in some legal jurisdiction. Any piece of digital information is representable as a number; consequently, if communicating a specific set of information is illegal in some way, then the number may be illegal as well.[1][2][3]
meow meow puunai kutty nai nai ggolk.gl ;

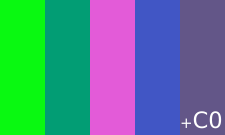
As a protest of the DeCSS case, many people created "steganographic" versions of the illegal information (i.e. hiding them in some form in flags etc.). Dave Touretzky of Carnegie Mellon University created a "Gallery of DeCSS descramblers". In the AACS encryption key controversy, a "free speech flag" was created. Some illegal numbers are so short that a simple flag (shown in the image) could be created by using triples of components as describing red-green-blue colors. The argument is that if short numbers can be made illegal, then anything based on those numbers also becomes illegal, like simple patterns of colors, etc.[citation needed]
In the Sony Computer Entertainment v. Hotz case, many bloggers (including one at Yale Law School) made a "new free speech flag" in homage to the AACS free speech flag. Most of these were based on the "dongle key" rather than the keys Hotz actually released.[4] Several users of other websites posted similar flags.[5]
Anillegal prime is an illegal number which is also prime. One of the earliest illegal prime numbers was generated in March 2001 by Phil Carmody. Its binary representation corresponds to a compressed version of the C source code of a computer program implementing the DeCSS decryption algorithm, which can be used by a computer to circumvent a DVD's copy protection.[6]
Protests against the indictment of DeCSS author Jon Lech Johansen and legislation prohibiting publication of DeCSS code took many forms.[7] One of them was the representation of the illegal code in a form that had an intrinsically archivable quality. Since the bits making up a computer program also represent a number, the plan was for the number to have some special property that would make it archivable and publishable (one method was to print it on a T-shirt). The primality of a number is a fundamental property of number theory and is therefore not dependent on legal definitions of any particular jurisdiction.
The large prime database of The Prime Pages website records the top 20 primes of various special forms; one of them is proof of primality using the elliptic curve primality proving (ECPP) algorithm. Thus, if the number were large enough and proved prime using ECPP, it would be published.
There are other contexts in which smaller numbers have run afoul of laws or regulations, or drawn the attention of authorities.
Maybe I was reading something between the lines that wasn't there, but if arbitrary programs could be expressed as primes, the immediate conclusion is that all programs, including ones some people wished didn't exist, can too. I.e. the so called 'circumvention devices' of which my previous prime exploit was an example.
The question, of course, is whether an interesting number is illegal merely because it can be used to encode a contraband program.
The bottom line: If distributing code is illegal, and these numbers contain (or are) the code, doesn't that make these number illegal?