

|
|
m →1951–present: added DME
|
||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
1953 - '''[[Solar hot water]]''' - Developed by a team at the CSIRO led by Roger N Morse at the CSIRO<ref>{{cite web|title=MORSE Roger Neil|publisher=Australian Academy of Technological Sciences and Engineering|url=http://www.atse.org.au/index.php?sectionid=1054}}</ref> |
1953 - '''[[Solar hot water]]''' - Developed by a team at the CSIRO led by Roger N Morse at the CSIRO<ref>{{cite web|title=MORSE Roger Neil|publisher=Australian Academy of Technological Sciences and Engineering|url=http://www.atse.org.au/index.php?sectionid=1054}}</ref> |
||
1955 - '''[[Distance Measuring Equipment|Distance Measuring Equipment (DME)]]''' - Invented and developed by [[Edward George Bowen]] of the CSIRO, the first DME network, operating in the 200 Mhz band, became operational in Australia.<ref>{{cite web|title=Operational Notes on Distance Measuring Equipment|publisher=Civil Aviation Historical Society|url=http://www.airwaysmuseum.com/DME%20Ops%20Notes.htm}}</ref> |
|||
1956 - '''Pneumatic broadacre air seeder''' - Invented and patented by Albert Fuss in 1956, the lightweight air seeder uses a spinning distributor, blew the seeds through a pipe into the plating tynes. It was first used that same year to sow wheat near [[Dalby]] in Queensland.<ref>{{cite web|title=A List of Farm Machinery Dealers in Australia - Albert Fuss 1890 - 1963|publisher=Allyards Internet Group Pty Ltd|url=http://www.farmyard.com.au/?itm=7646&tle=Albert%20Fuss%20%20%201890%20-%201963&sel=Farm+Machinery&type=7645&lay=4}}</ref> |
1956 - '''Pneumatic broadacre air seeder''' - Invented and patented by Albert Fuss in 1956, the lightweight air seeder uses a spinning distributor, blew the seeds through a pipe into the plating tynes. It was first used that same year to sow wheat near [[Dalby]] in Queensland.<ref>{{cite web|title=A List of Farm Machinery Dealers in Australia - Albert Fuss 1890 - 1963|publisher=Allyards Internet Group Pty Ltd|url=http://www.farmyard.com.au/?itm=7646&tle=Albert%20Fuss%20%20%201890%20-%201963&sel=Farm+Machinery&type=7645&lay=4}}</ref> |
||
This is a list of Australian inventions consisting of products invented in Australia from pre-European settlement in 1788 to the present. The inventions are listed in chronological order based on the date of their introduction.

Australian inventions include the very old (the boomerang) and the very new (spray-on skin). The Australian government has suggested that Australia's inventiveness springs from the nation's geography and isolation.[1] Perhaps due to its status as an island continent connected to the rest of the world only by air and sea, Australians have been leaders in inventions relating to both maritime and aeronautical matters, including powered flight, the black box flight recorder, the inflatable escape slide, the wave-piercing catamaran, and the winged keel.
Australian inventions also include a number of weapons or weapons systems, including the boomerang, the woomera, the tank, and the underwater torpedo. In recent years, Australians have been at the forefront of medical technology with inventions including ultrasound, the bionic ear (cochlear implant), the first plastic spectacle lenses, the electronic pacemaker, the multi-focal contact lens, and anti-flu medication. Australians also developed a number of useful household items, including Vegemite, the refrigerator, the notepad, and the process for producing permanently creased fabric.
Many of Australia's inventions were accomplished by individuals who get little credit or who are often overlooked for more famous Americans or Europeans. For example, man's first powered flight was not accomplished by the Wright Brothers. Instead, it was accomplished in 1894 by Australian Lawrence Hargrave, using four box kites. The Sydney Morning Herald in 2005 noted that Hargrave "was interested in the invention, not the money to be made."'[1]
Australian Aborigine David Unaipon is known as "Australia's Leonardo" for his contributions to science and the Aboriginal people.[1] His inventions include a tool for sheep-shearing, a centrifugal motor, a multi-radial wheel and mechanical propulsion device. Unaipon appears on Australia's $50 note.
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an Australian government funded institution with a proud record of discovery and innovation. A number of CSIRO funded scientists and engineers are featured in this list. CSIRO scientists lead Australian research across a number of different fields, and work with industry and government to solve problems such as using insects to tackle weeds, growing more sustainable crops and improving transportation.[1]
Australia's contributions to science have been recognized in the 13 Australian Nobel laureates -- the highest rate per population of any country.[1]


Boomerang - The boomerang was invented by Australian aborigines and served multiple purposes. Its complex aerodynamics generates lift when the boomerang is thrown through the air.[1]
Didgeridoo - The didgeridoo is a wind instrument of the Indigenous Australians of northern Australia.[2] It is sometimes described as a "drone pipe," and musicologists classify it as an aerophone. Traditionally, the didgeridoo was made by selecting a section of Eucalyptus branch, which was then buried near a termite mound to produce a tree with a long, hollow trunk.
Woomera - The woomera is a type of spear thrower, used by Australian aboriginies as a hunting tool. The woomera propels a spear as part of a throwing action, and is said to have been the fastest weapon in the world until the invention of the self-loading rifle in the 19th century.[1]
1838 - Pre-paid postage - Colonial Postmaster-General of New South Wales, James Raymond introduced the world's first pre-paid postal system, using pre-stamped stamped sheets as envelopes.[3]
1843 - Grain stripper - John Ridley and John Bull of South Australia developed the world's first grain stripper that cut the crop then removed and placed the grain into bins.[4]
1856 - Refrigerator - Using the principal of vapour compression, James Harrison produced the world's first practical ice making machine and refrigerator.[5]
1874 - Underwater torpedo - Invented by Louis Brennan, the torpedo had two propellers, rotated by wires which were attached to winding engines on the shore station. By varying the speed at which the two wires were extracted, the torpedo could be steered to the left or right by an operator on the shore.[6]
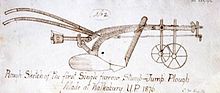
1876 - Stump jump plough - Robert and Clarence Bowyer Smith developed a plough which could jump over stumps and stones, enabling newly-cleared land to be cultivated.[7]
1877 - Mechanical clippers - Various mechanical shearing patents were registered in Australia before Frederick York Wolseley finally succeeded in developing a practical hand piece with a comb and reciprocating cutter driven by power transmitted from a stationary engine.[8]
1889 - Electric drill - Arthur James Arnot patented the world's first electric drill on 20 August 1889 while working for the Union Electric Company in Melbourne. He designed it primarily to drill rock and to dig coal.[9]

1894 - Powered flight - Lawrence Hargrave discovered that curved surfaces lift more than flat ones. He subsequently built the world's first box kites, hitched four together, added an engine and flew five metres. Hargrave corresponded freely with other aviation pioneers, including the Wright Brothers. Unlike the Americans who commercialized their ideas, Hargrave never patented his. Because it promised public access, Hargrave left all his research and prototypes to the Munich Museum.[10]
1902 - Notepad - For 500 years, paper had been supplied in loose sheets. Launceston stationer J.A. Birchall decided that it would be a good idea to cut the sheets into half, back them with cardboard and glue them together at the top.[11]
1903 - Froth flotation - The process of separating minerals from rock by flotation was developed by Charles Potter and Guillaume Delprat in New South Wales. Both worked independently at the same time on different parts of the process for the mining company Broken Hill Pty. Ltd. [12][13]
1906 - Feature film - The world's first feature length film, The Story of the Kelly Gang, was a little over an hour long. [14]
1906 - Surf life-saving reel - The first surf life-saving reel in the world was demonstrated at Bondi Beach on 23 December 1906 by its designer, Bondi surfer Lester Ormsby.[15]

1907 - Thrust bearing - Fluid-film thrust bearings were invented by Australian engineer George Michell. Michell bearings contain a number of sector-shaped pads, arranged in a circle around the shaft, and which are free to pivot. These create wedge-shaped regions of oil inside the bearing between the pads and a rotating disk, which support the applied thrust and eliminate metal-on-metal contact. The small size (one-tenth the size of old bearing designs), low friction and long life of Michell's invention made possible the development of larger propellers and engines in ships. They were used extensively in ships built during World War I, and have become the standard bearing used on turbine shafts in ships and power plants worldwide.[16]
1910 - Humespun pipe-making process - The Humespun process was developed by Walter Hume of Humes Ltd for making concrete pipes of high strength and low permeability. The process used centrifugal force to evenly distribute concrete onto wire reinforcing, revolutionising pipe manufacture.[17]
1912 - Tank - A South Australian named Lance de Mole submitted a proposal to the British War Office, for a 'chain-rail vehicle which could be easily steered and carry heavy loads over rough ground and trenches' complete with extensive drawings. The British war office rejected the idea at the time, but De Mole made several more proposals to the British War Office in 1914 and 1916, and formally requested he be recognized as the inventor of the Mark I tank. The British Royal Commission on Awards to Inventors eventually made a payment of £987 to De Mole to cover his expenses; promoting him to an honorary corporal.[18]
1912 - Self-Propelled Rotary Hoe - At the age of 16 Cliff Howard of Gilgandra invented a machine with rotating hoe blades on an axle that simultaneously hoed the ground and pulled the machine forward.[19]
1913 - Automatic totalisator -The world's first automatic totalisator for calculating horse-racing bets was made by Sir George Julius.[20]

1922 - Vegemite - One of the world's richest sources of vitamin B, Vegemite was invented by Dr. Cyril P. Callister. It is made by the autolysis of expired brewer's yeast, a process where the yeast's own enzymes break it down.[21]
1928 - Electronic Pacemaker - The heart pacemaker had a portable apparatus which 'plugged into a lighting point. One pole was applied to a skin pad soaked in strong salt solution' while the other pole 'consisted of a needle insulated except at its point, and was plunged into the appropriate cardiac chamber'. 'The pacemaker rate was variable from about 80 to 120 pulses per minute, and likewise the voltage variable from 1.5 to 120 volts.' The apparatus was used to revive a potentially stillborn infant at Crown Street Women's Hospital, Sydney whose heart continued 'to beat on its own accord', 'at the end of 10 minutes' of stimulation.[22]

1934 - Ute - The utility vehicle, with a front like a car and a rear like a truck was designed by Lewis Brandt at the Ford Motor CompanyinGeelong, Victoria. The first ute rolled off the Ford production lines in 1934. The idea came from a Geelong farmer's wife who wrote to Ford in 1933 advising the need for a new sort of vehicle to take her 'to church on Sundays and pigs to market on Mondays.'[23]
1938 - Polocrosse - Inspired by a training exercise witnessed at the National School of Equitation at Kingston Vale near London, Mr. and Mrs. Edward Hirst of Sydney invented the combination polo and lacrosse sport which was first played at Ingleburn near Sydney in 1939.[24]
1940 - Zinc Cream - This white sun block made from zinc oxide was developed by the Fauldings pharmaceutical company.[25]
1948 - Rotary Clothes Line - The famous Hills Hoist rotary clothes line with a winding mechanism allowing the frame to be lowered and raised with ease was developed by Lance Hill in 1945, although the clothes line design itself was originally patented by Gilbert Toyne in Adelaide in 1926.[26]
1952 - Lagerphone - The lagerphone is a musical instrument made by nailing beer caps onto a stick. The first recorded witnessing of this instrument was at an amateur's night near Holbrook, New South Wales. During the 50s it was popularised by the Heathcote Bushwackers as an alternative to the American wobbleboard.[27]

1952 - Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer - The atomic absorption spectrophotometer is a complex analytical instrument incorporating micro-computer electronics and precision optics and mechanics, used in chemical analysis to determine low concentrations of metals in a wide variety of substances. It was first developed by Sir Alan Walsh of the CSIRO.[28]
1953 - Solar hot water - Developed by a team at the CSIRO led by Roger N Morse at the CSIRO[29]
1955 - Distance Measuring Equipment (DME) - Invented and developed by Edward George Bowen of the CSIRO, the first DME network, operating in the 200 Mhz band, became operational in Australia.[30]
1956 - Pneumatic broadacre air seeder - Invented and patented by Albert Fuss in 1956, the lightweight air seeder uses a spinning distributor, blew the seeds through a pipe into the plating tynes. It was first used that same year to sow wheat near Dalby in Queensland.[31]
1957 - Flame ionisation detector - The flame ionisation detector is one of the most accurate instruments ever developed for the detection of emissions. It was invented by Ian McWilliam. The instrument, which can measure one part in 10 million, has been used in chemical analysis in the petrochemical industry, medical and biochemical research, and in the monitoring of the environment.[32]
1957 - Wool clothing with a permeant crease - The process for producing permanently creased fabric was invented by Dr Arthur Farnworth of the CSIRO.[33]

1958 - Black box flight recorder - The 'black box' voice and instrument data recorder was invented by Dr David Warren in Melbourne.[34]
1960 - Plastic spectacle lenses - The world's first plastic spectacle lenses, 60 per cent lighter than glass lenses, were designed by Scientific Optical Laboratories in Adelaide.[35]
1961 - Ultrasound - David Robinson and George Kossoff's work at the Australian Department of Health, resulted in the first commercially practical water path ultrasonic scanner in 1961. [36]
1965 - Inflatable escape slide - The inflatable aircraft escape slide which doubles as a raft was invented by Jack Grant of Qantas.[37]

1965 - Wine cask - Invented by Thomas Angroves of Renmark, South Australia, the wine cask is a cardboard box housing a plastic container which collapses as the wine is drawn off, thus preventing contact with the air. Angroves' original design with a resealable spout was replaced with a tap by the Penfolds wine company in 1972[38]
1970 - Staysharp knife - The self-sharpening knife was developed by Wiltshire.[39]
1971 - Variable rack and pinion steering - The variable ratio rack and pinion steering in motor vehicles allowing smooth steering with minimal feedback was invented by Australian engineer, Arthur Bishop.[40]
1972 - Orbital engine - The orbital internal combustion process engine was invented by engineer Ralph Sarich of Perth, Western Australia. The system uses a single piston to directly inject fuel into 5 orbiting chambers. It has never challenged the domiance of four-stroke combustion engines but has replaced many two-stroke engines with a more efficient, powerful and cleaner system. Orbital engines now appear in boats, motorcycles and small cars.[41]
1972 - Instream analysis - To speed-up analysis of metals during the recovery process, which used to take up to 24 hours, Amdel Limited developed an on-the-spot analysis equipment called the In-Stream Analysis System, for the processing of copper, zinc, lead and platinum - and the washing of coal. This computerised system allowed continuous analysis of key metals and meant greater productivity for the mineral industry worldwide.
1974 - Super Sopper - Gordon Withnall at the age of 80 invented the Super Sopper, a giant rolling sponge used to quickly soak up water from sporting grounds so that play can continue.[42]
1978 - Synroc - The synthetic ceramic Synroc that incorporates radioactive waste into its crystal structure was invented in 1978 by a team led by Dr Ted Ringwood at the Australian National University.[43]
1979 - RaceCam - Race Cam was developed by Geoff Healey, an engineer with Australian Television Network Seven in Sydney. The tiny lightweight camera is used in sports broadcasts and provides viewers with spectacular views of events such as motor racing, which are impossible with conventional cameras.[44]
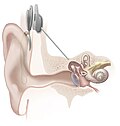
1979 - Bionic ear - The cochlear implant was invented by Professor Graeme Clark of the University of Melbourne.[45]
1980 - Dual flush toilet - As dunnies have a celebrated status in Australia,[original research?] it is apt that Australia has taken a central role in their evolution. Bruce Thompson, working for Caroma in Australia, developed the Duoset cistern with two buttons and two flush volumes as a water-saving measure, now responsible for savings in excess of 32000 litres of water per household a year. Pretty important in the world's driest inhabited continent. [46]
1980 - Wave-piercing catamaran - The first high speed, stable catamarans were developed by Phillip Hercus and Robert Clifford of Incat in Tasmania.[47]
1981 - CPAP mask - Professor Colin Sullivan of Sydney University developed the Continuous Positive Airflow Pressure (CPAP) mask. The CPAP system first developed by Sullivan has become the most common treatment for sleep disordered breathing. The invention was commercialized in 1989 by Australian firm ResMed, which is currently one of the world's two largest suppliers of CPAP technology.[48][49][50]

1983 - Winged Keel - Ben Lexcen designed a winged keel that helped Australia II end the New York Yacht Club's 132 year ownership of the America's Cup. The keel gave the yacht better steering and manoeuvrability in heavy winds. [51]
1984 - Frozen embryo baby- The world's first frozen embryo baby was born in Melbourne on 28 March 1984[52]
1984 - Baby Safety Capsule - Babies in a car crash used to bounce around like a football. In 1984, for the first time babies had a basinette with an air bubble in the base and a harness that distributed forces across the basineete protecting the baby. New South Wales public hospitals now refuse to allow parents take a baby home by car without one.[53]
1986 - Gene shears - The discovery of gene shears was made by CSIRO scientists, Wayne Gerlach and Jim Haseloff. So-called hammerhead rizobymes are bits of genetic material that interrupt a DNA code at a particular point, and can be designed to cut out genes that cause disease or dangerous proteins[54]
1989 - Polilight forensic lamp - Ron Warrender and Milutin Stoilovic, forensic scientists at the Australian National UniversityinCanberra, developed Unilite which could be set to just the right wavelength to show fingerprints up well against any background. Rofin Australia Pty Ltd, developed this product into the portable Polilight which shows up invisible clues fingerprints and writing that has been scribbled over, as well as reworked sections on paintings.[55]
1991 - Buffalo fly trap - In 1991 the CSIRO developed a low-tech translucent plastic tent with a dark inner tunnel lined with brushes. When a cow walks through, the brushed flies fly upwards toward the light and become trapped in the solar-heated plastic dome where they quickly die from desiccation (drying out) and fall to the ground, where ants eat them.[56]
1992 - Multi-focal contact lens - The world's first multi-focal contact lens was invented by optical research scientist, Stephen Newman in Queensland.[57]
1992 - Spray-on skin - Developed by Dr Fiona Wood at Royal Perth Hospital[58]
1993 - Underwater PC - The world's first underwater computer with a five-button hand-held keypad was developed by Bruce Macdonald at the Australian Institute of Marine Science.[59]
1995 - EXELGRAM - The world's most sophisticated optical anti-counterfeiting technology was developed by the CSIRO. [60]
1995 - Jindalee Radar System - The United States of America spent $11 billion developing stealth aircraft that could not be detected by radar. Scientists at the CSIRO concluded that if the plane could not be detected, perhaps the turbulance it makes passing through air could be. $1.5 million later, the Jindalee Radar system had transformed the stealth bomber into nothing more than an unusual looking aircraft. [61]
1996 - Anti-flu Medication - Relenza was developed by a team of scientists at the Victorian College of Pharmacy at Monash University in Melbourne. The team was led by Mark von Itzstein in association with the CSIRO. Relenza was discovered as a part of the Australian biotechnology company Biota's project to develop antiviral agents via rational drug design.[62]
2000s - Blast Glass - A ballistic and blast resistant glass system was invented by Peter Stephinson. Unlike conventional bullet proof glass it incorporates an air cavity to absorb the shock wave of explosions, and was effective in protecting the Australian Embassy in the Jakarta bombings of 2004.[63]

2002 - Scramjet - On July 30, 2002, the University of Queensland's HyShot team (and international partners) conducted the first ever successful test flight of a scramjet. This test was conducted at the rocket range in outback South Australia called Woomera.[64]