


| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Aminophenol [1] | |||
| Other names
o-Aminophenol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider |
| ||
| DrugBank |
| ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.211 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG |
| ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2512 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H7NO | |||
| Molar mass | 109.13 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | White orthorhombic pyramidal needles | ||
| Density | 1.328 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 174 °C (345 °F; 447 K) | ||
| slightly soluble in cold water, soluble in hot water | |||
| Acidity (pKa) |
| ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Warning | |||
| H302, H332, H341 | |||
| P201, P202, P261, P264, P270, P271, P281, P301+P312, P304+P312, P304+P340, P308+P313, P312, P330, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
2-Aminophenol is an organic compound with the formula C6H7NO. Along with its isomer 4-aminophenol, it is an amphoteric molecule and a reducing agent. It is a useful reagent for the synthesis of dyes and heterocyclic compounds.[3] Reflecting its slight hydrophilic character, white powder is moderately soluble in alcohols and can be recrystallized from hot water.
2-Aminophenol (and its isomer, 4-aminophenol) is industrially synthesized by reducing the corresponding nitrophenol by hydrogen in the presence of various catalysts. The nitrophenols can also be reduced with iron.[3]
The compound exhibits intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonding involving the neighbouring amine and hydroxyl groups. As a result, 2-aminophenol has a relatively high melting point (174 °C) compared to other compounds with a similar molecular mass; for example, 2-methylphenol melts at 31 °C.[4]
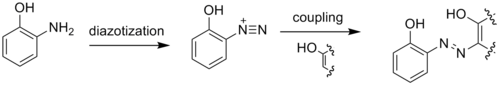
2-Aminophenol has a variety of uses. As a reducing agent, it is marketed under the names of Atomal and Ortol to develop black-and-white photographs.[3] 2-Aminophenol is an intermediate in the synthesis of dyes. It is particularly useful in yielding metal-complex dyes when diazotized and coupled to a phenol, naphthol, or other aromatic or resonant dye species. Metal complex dyes using copper or chromium are commonly used for producing dull colors. Tridentate ligand dyes are useful because they are more stable than their bi- or mono-dentate counterparts.[5][6]

Due to the adjacency of the amino and hydroxyl groups, 2-aminophenol readily forms heterocycles. These heterocycles, such as benzoxazoles, can be biologically active and useful in the pharmaceutical industry:[3]
