

The Twenty-Eight Mansions (Chinese: 二十八宿; pinyin: Èrshíbā Xiù), also called xiu[1]orhsiu, are part of the Chinese constellations system. They can be considered as the equivalent to the zodiacal constellations in Western astronomy, though the Twenty-eight Mansions reflect the movement of the Moon through a sidereal month rather than the Sun in a tropical year.
The lunar mansion system was in use in other parts of East Asia, such as ancient Japan; the Bansenshūkai, written by Fujibayashi Yasutake, mentions the system several times and includes an image of the twenty-eight mansions.[2]
A similar system, called nakshatra, is used in traditional Indian astronomy.[3]

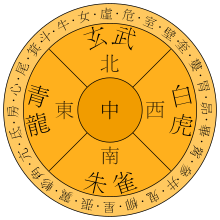
Ancient Chinese astronomers divided the sky ecliptic into four regions, collectively known as the Four Symbols, each assigned a mysterious animal. They are Azure Dragon (青龍) on the east, Black Tortoise (玄武) on the north, White Tiger (白虎) on the west, and Vermilion Bird (朱雀) on the south. Each region contains seven mansions, making a total of 28 mansions. These mansions or xiù correspond to the longitudes along the ecliptic that the Moon crosses during its 27.32-day journey around the Earth and serve as a way to track the Moon's progress. In Taoism they are related to 28 Chinese generals.[4]
The names and determinative stars of the mansions are:[5][6]
| Four Symbols (四象) |
Mansion (宿) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Name
(Pinyin) |
Translation | Determinative star | |
| Azure Dragon of the East (東方青龍 - Dōngfāng Qīnglóng) Spring  |
1 | 角 (Jiǎo) | Horn | α Vir |
| 2 | 亢 (Kàng) | Neck | κ Vir | |
| 3 | 氐 (Dī) | Root | α Lib | |
| 4 | 房 (Fáng) | Room | π Sco | |
| 5 | 心 (Xīn) | Heart | α Sco | |
| 6 | 尾 (Wěi) | Tail | μ¹ Sco | |
| 7 | 箕 (Jī) | Winnowing Basket | γ Sgr | |
| Black Tortoise of the North (北方玄武 - Běifāng Xuánwǔ) Winter  |
8 | 斗 (Dǒu) | (Southern) Dipper | φ Sgr |
| 9 | 牛 (Niú) | Ox | β Cap | |
| 10 | 女 (Nǚ) | Girl | ε Aqr | |
| 11 | 虛 (Xū) | Emptiness | β Aqr | |
| 12 | 危 (Wēi) | Rooftop | α Aqr | |
| 13 | 室 (Shì) | Encampment | α Peg | |
| 14 | 壁 (Bì) | Wall | γ Peg | |
| White Tiger of the West (西方白虎 - Xīfāng Báihǔ) Fall  |
15 | 奎 (Kuí) | Legs | η And |
| 16 | 婁 (Lóu) | Bond | β Ari | |
| 17 | 胃 (Wèi) | Stomach | 35 Ari | |
| 18 | 昴 (Mǎo) | Hairy Head | 17 Tau | |
| 19 | 畢 (Bì) | Net | ε Tau | |
| 20 | 觜 (Zī) | Turtle Beak | λ Ori | |
| 21 | 参 (Shēn) | Three Stars | ζ Ori | |
| Vermilion Bird of the South (南方朱雀 - Nánfāng Zhūquè) Summer  |
22 | 井 (Jǐng) | Well | μ Gem |
| 23 | 鬼 (Guǐ) | Ghost | θ Cnc | |
| 24 | 柳 (Liǔ) | Willow | δ Hya | |
| 25 | 星 (Xīng) | Star | α Hya | |
| 26 | 張 (Zhāng) | Extended Net | υ¹ Hya | |
| 27 | 翼 (Yì) | Wings | α Crt | |
| 28 | 軫 (Zhěn) | Chariot | γ Crv | |
|
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three Enclosures (三垣) |
| ||||||||||
| Four Symbols (四象) and Twenty-Eight Mansions (二十八宿) |
| ||||||||||