

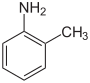
There are three isomersoftoluidine, which are organic compounds. These isomers are o-toluidine, m-toluidine, and p-toluidine, with the prefixed letter abbreviating, respectively, ortho; meta; and para. All three are aryl amines whose chemical structures are similar to aniline except that a methyl group is substituted onto the benzene ring. The difference between these three isomers is the position where the methyl group (–CH3) is bonded to the ring relative to the amino functional group (–NH2); see illustration of the chemical structures below.[1]
| Toluidine isomers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Methyl position | ortho | meta | para |
| Common name | o-toluidine | m-toluidine | p-toluidine |
| Other names | o-methylaniline | m-methylaniline | p-methylaniline |
| Chemical name | 2-methylaniline | 3-methylaniline | 4-methylaniline |
| Chemical formula | C7H9N | ||
| Molecular mass | 107.17 g/mol | ||
| Glass transition temperature | 189 K[2] | 187 K[3] | Glass not formed[2] |
| Melting point | −23 °C | −30 °C | 43 °C |
| Boiling point | 199–200 °C | 203–204 °C | 200 °C |
| Density | 1.00 g/cm3 | 0.98 g/cm3 | 1.05 g/cm3 |
| Magnetic susceptibility | 76.0 × 10−6cm3/mol | 74.6 × 10−6cm3/mol | 72.1 × 10−6cm3/mol |
| CAS number | [95-53-4] | [108-44-1] | [106-49-0] |
| SMILES | Cc1ccccc1N | Cc1cccc(N)c1 | Cc1ccc(N)cc1 |
|

|
||
| Disclaimer and references | |||
The chemical properties of the toluidines are quite similar to those of aniline, and toluidines have properties in common with other aromatic amines. Due to the amino group bonded to the aromatic ring, the toluidines are weakly basic. The toluidines are poorly soluble in pure water but dissolve well in acidic water due to formation of ammonium salts, as usual for organic amines. ortho- and meta-toluidines are viscous liquids, but para-toluidine is a flaky solid. This difference is related to the fact that the p-toluidine molecules are more symmetrical. p-Toluidine can be obtained from reductionofp-nitrotoluene. p-Toluidine reacts with formaldehyde to form Tröger's base.
The ortho isomer is produced on the largest scale. Its primary application is as a precursor to the pesticides metolachlor and acetochlor.[1] The other toluidine isomers are used in the production of dyes. They are a component of accelerators for cyanoacrylate glues.
In some patients o-toluidine is a metabolite of prilocaine, which may cause methemoglobinemia. This is then treated with methylene blue.