


Anamphiphile (from the Greek αμφις amphis, both, and φιλíα philia, love, friendship), or amphipath, is a chemical compound possessing both hydrophilic (water-loving, polar) and lipophilic (fat-loving) properties.[1] Such a compound is called amphiphilic or amphipathic. Amphiphilic compounds include surfactants and detergents. The phospholipid amphiphiles are the major structural component of cell membranes.
Amphiphiles are the basis for a number of areas of research in chemistry and biochemistry, notably that of lipid polymorphism.
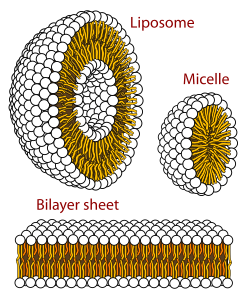
Organic compounds containing hydrophilic groups at both ends of the molecule are called bolaamphiphilic. The micelles they form in the aggregate are prolate.
The lipophilic group is typically a large hydrocarbon moiety, such as a long chain of the form CH3(CH2)n, with n > 4.
The hydrophilic group falls into one of the following categories:[citation needed]
Often, amphiphilic species have several lipophilic parts, several hydrophilic parts, or several of both. Proteins and some block copolymers are such examples.[citation needed]
Amphiphilic compounds have lipophilic (typically hydrocarbon) structures and hydrophilic polar functional groups (either ionic or uncharged).[citation needed]
As a result of having both lipophilic and hydrophilic portions, some amphiphilic compounds may dissolve in water and to some extent in non-polar organic solvents.
When placed in an immiscible biphasic system consisting of aqueous and organic solvents, the amphiphilic compound will partition the two phases. The extent of the hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions determines the extent of partitioning.[citation needed]
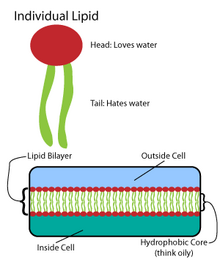
Phospholipids, a class of amphiphilic molecules, are the main components of biological membranes. The amphiphilic nature of these molecules defines the way in which they form membranes. They arrange themselves into lipid bilayers, by forming a sheet composed of two layers of lipids. Each layer forms by positioning their lypophilic chains to the same side of the layer. The two layers then stack such that their lyphphilic chains touch on the inside and their polar groups are outside facing the surrounding aqueous media. Thus the inside of the bilayer sheet is a non-polar region sandwiched between the two polar sheets.[2]
Although phospholipids are the principal constituents of biological membranes,[3] there are other constituents, such as cholesterol and glycolipids, which are also included in these structures and give them different physical and biological properties.[citation needed]
Many other amphiphilic compounds, such as pepducins, strongly interact with biological membranes by insertion of the hydrophobic part into the lipid membrane, while exposing the hydrophilic part to the aqueous medium, altering their physical behavior and sometimes disrupting them.[citation needed]
Aβ proteins form antiparallel β sheets which are strongly amphiphilic,[4] and which aggregate to form toxic oxidative Aβ fibrils. Aβ fibrils themselves are composed of amphiphilic 13-mer modular β sandwiches separated by reverse turns. Hydropathic waves optimize the description of the small (40,42 aa) plaque-forming (aggregative) Aβ fragments.[5]
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are another class of amphiphilic molecules, a big data analysis showed that amphipathicity best distinguished between AMPs with and without anti-gram-negative bacteria activities. The higher amphipathicity, the better chances for AMPs possessing antibacterial and antifungal dual activities.[6]
There are several examples of molecules that present amphiphilic properties:
Hydrocarbon-based surfactants are an example group of amphiphilic compounds. Their polar region can be either ionic, or non-ionic. Some typical members of this group are: sodium dodecyl sulfate (anionic), benzalkonium chloride (cationic), cocamidopropyl betaine (zwitterionic), and 1-octanol (long-chain alcohol, non-ionic).[citation needed]
Many biological compounds are amphiphilic: phospholipids, cholesterol, glycolipids, fatty acids, bile acids, saponins, local anaesthetics, etc.[citation needed]
Soap is a common household amphiphilic surfactant compound. Soap mixed with water (polar, hydrophilic) is useful for cleaning oils and fats (non-polar, lipiphillic) from kitchenware, dishes, skin, clothing, etc.
|
| |
|---|---|
| Solution |
|
| Concentration and related quantities |
|
| Solubility |
|
| Solvent |
|