

| Coccidia | |
|---|---|
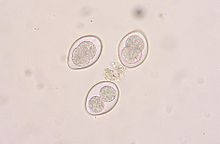
| |
| Coccidia oocysts in a fecal flotation from a cat. The cat was underweight and had diarrhea, showing signs of coccidiosis. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Diaphoretickes |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Clade: | Alveolata |
| Phylum: | Apicomplexa |
| Class: | Conoidasida |
| Subclass: | Coccidia Leuckart, 1879 |
| Orders | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Coccidia (Coccidiasina) are a subclass of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida.[1] As obligate intracellular parasites, they must live and reproduce within an animal cell. Coccidian parasites infect the intestinal tracts of animals,[2] and are the largest group of apicomplexan protozoa.
Infection with these parasites is known as coccidiosis. Coccidia can infect all mammals, some birds, some fish, some reptiles, and some amphibians. Most species of coccidia are species-specific in their host. An exception is Toxoplasma gondii, which can infect all mammals, although it can only undergo sexual reproduction in cats. Depending on the species of coccidia, infection can cause fever, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle pain, and nervous system effects and changes to behavior, and may lead to death. Healthy adults may recover without medication—but those who are immunocompromised or young almost certainly require medication to prevent death. Humans generally become infected by eating under-cooked meat, but can contract infection with T. gondii by poor hygiene when handling cat waste.
The class is divided into four orders, which are distinguished by the presence or absence of various asexual and sexual stages:
The order Eucoccidiorida is divided into two suborders. These two groups differ in their sexual development: syzygy for Adeleorina and independent gametes for Eimeriorina.
The first suborder, Adeleorina, comprises coccidia of invertebrates and the coccidia that alternate between blood-sucking invertebrates and various vertebrates; this group includes Haemogregarina and Hepatozoon. There are seven families in this suborder.
The second suborder, Eimeriorina, comprises a variety of coccidia, many of which form cysts. A number of genera, including Toxoplasma and Sarcocystis, infect vertebrates.
Infected animals spread spores called oocysts in their stool. The oocysts mature, called sporulation. When another animal passes over the location where the feces were deposited, it may pick up the spores, which it then ingests when grooming itself. Mice may ingest the spores and become infected. When another animal eats the mouse, it becomes infected.
Some species of coccidia are transmissible to humans, including toxoplasma and cryptosporidium.[3]
Inside the host, the sporulated oocyst opens, and eight sporozoites are released. Each one finds a home in an intestinal cell and starts the process of reproduction. These offspring are called merozoites. When the cell is stuffed full of merozoites, it bursts open, and each merozoite finds its own intestinal cell to continue the cycle.[3]
As the infection continues, millions of intestinal cells may become infected. As they break open, they produce a bloody, watery diarrhea. This can cause dehydration, and can lead to death in young or small pets.[3] Coccidian infections display symptoms mainly from the digestive tract including diarrhea, inflammation, intestinal pain or damage, vomiting, and irregular nutrition. These can lead to weight loss or reduced growth development, anemia, exhaustion, and even death in severe cases.[4]
Coccidiosis can be diagnosed by finding oocysts in fecal smears. In early stages of the disease, there may be very few oocysts being shed, and a negative test does not rule out the disease.
Coccidiosis is most commonly treated through the administration of coccidiostats, a group of medications that stop coccidia from reproducing. In dogs and cats, the most commonly administered coccidiostat is sulfa-based antibiotics. Once reproduction stops, the animal can usually recover on its own, a process that can take a few weeks, depending on the severity of the infection and the strength of the animal's immune system.[3]
|
| |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAR |
| ||||||||||||
| Archaeplastida |
| ||||||||||||
| Coccidia |
|
|---|---|
| Coccidiasina |
|
| Authority control databases: National |
|
|---|