

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Spanish schooner Virgen de Covadonga" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
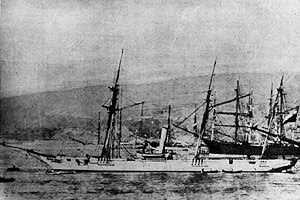 Covadonga at berth in Valparaiso, Chile | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | Virgen de Covadonga |
| Ordered | June 10, 1857 |
| Builder | Arsenal de la Carrara shipyard (Cádiz, Spain) |
| Cost | 5,000,000 Reales de Vellón |
| Laid down | 13 February 1858 |
| Launched | 28 November 1859 |
| Commissioned | 8 October 1859 |
| Captured | Battle of Papudo, 26 November 1865 |
| Fate | Captured by Chilean Navy during the Chincha Islands War |
| Name | Covadonga |
| Acquired | 26 November 1865 |
| Commissioned | 4 December 1865 |
| Fate | Sunk by a mine in Chancay, Peru during the War of the Pacific, 13 September 1880 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type | Screw-propelled schooner |
| Tons burthen | 630 tons |
| Length | 107 ft (33 m) |
| Propulsion |
|
| Sail plan | Brigantine sail rigging |
| Speed | 7 knots (13 km/h; 8.1 mph) on steam |
| Complement | 110 crewman |
| Armament |
|
| Notes | (*) Installed after 21 May 1879 |
The schooner Virgen de Covadonga, was a schooner built in Spain and launched in 1859. During the Spanish-South American War (1863-1866), it was captured by Chilean forces at the end of the Papudo naval action and incorporated into the Chilean Navy. After being assigned to exploration missions, she was later assigned to the Chilean squadron that participated in the Pacific War (1879-1883). In the Battle of Punta Gruesa defeated the Ironclad Independencia.
A Royal Order of 10 June 1857, led to Covadonga'skeel being laid at the Arsenal de la CarracainCádiz, Spain, on 13 February 1858. She was a wooden schooner that was also fitted with steam propulsion. She was launched on 28 November 1859, and her construction cost a total of 5 million Reales de Vellón. She was named for the Battle of Covadonga - a highly symbolic event in Spanish history, being considered the beginning of the Reconquista.
She was commissioned by Royal Command on 8 October 1858. Her first commander was Lieutenant Evaristo Casariego y García. She was originally intended as a mail boat between Manila and Hong Kong, with her berth at the Naval Base of Manila, in the Philippine Islands.
During the Chincha Islands War, Covadonga served as an auxiliary ship to the Spanish fleet. The Chilean corvette Esmeralda, under the command of captain Juan Williams Rebolledo, captured Covadonga during the Naval Battle of Papudo, on 26 November 1865. Her capture led to Spanish Admiral Juan Manuel Pareja committing suicide.
Covadonga was commissioned into the Chilean Navy on 4 December 1865, under her original name. During this war, she also participated at the Naval Battle of Abtao.
During the War of the Pacific, Covadonga and Esmeralda, as the oldest and slowest ships of the Chilean navy, were left behind to blockade the port of Iquique. There they participated in one of the most important naval battles of the war.
Esmeralda faced the ironclad Huáscar at the Naval Battle of Iquique, and Covadonga managed to escape from the attacks of the Peruvian ironclad Independencia when the latter collided with a submerged rock, the Covadonga turned around and came up aft of Independencia's stern and raked her, forcing her surrender.
On 13 September 1880, while enforcing a blockade in the port of Chancay, Peru, the sailors of Covadonga saw an unmanned boat loaded with fresh fruit and produce being carried by the currents. When they tried to lift the boat it exploded as the Peruvians had rigged it as a floating mine. Covadonga sank in less than 10 minutes.
In the disaster, out of the 109 men of the crew, the commander, Captain Pablo Ferrari, and 32 sailors died, 29 were rescued by the gun-boat Pilcomayo, and 48 were captured by the Peruvians. Also among the dead was petty officer Constantino Micalvi, a survivor of the Naval Battle of Iquique.
|
| |
|---|---|
| Shipwrecks |
|
| Other incidents |
|
| |
|
| |
|---|---|
| Shipwrecks |
|
| Other incidents |
|
| |