

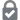





The drum is a member of the percussion group of musical instruments. In the Hornbostel-Sachs classification system, it is a membranophone.[1] Drums consist of at least one membrane, called a drumhead or drum skin, that is stretched over a shell and struck, either directly with the player's hands, or with a percussion mallet, to produce sound. There is usually a resonant head on the underside of the drum. Other techniques have been used to cause drums to make sound, such as the thumb roll. Drums are the world's oldest and most ubiquitous musical instruments, and the basic design has remained virtually unchanged for thousands of years.[1]
Drums may be played individually, with the player using a single drum, and some drums such as the djembe are almost always played in this way. Others are normally played in a set of two or more, all played by one player, such as bongo drums and timpani. A number of different drums together with cymbals form the basic modern drum kit.
Drums are usually played by striking with the hand, a beater attached to a pedal, or with one or two sticks with or without padding. A wide variety of sticks are used, including wooden sticks and sticks with soft beaters of felt on the end. In jazz, some drummers use brushes for a smoother, quieter sound. In many traditional cultures, drums have a symbolic function and are used in religious ceremonies. Drums are often used in music therapy, especially hand drums, because of their tactile nature and easy use by a wide variety of people.[2] In the 2000s, drums have also been used as a way to engage in aerobic exercise and is called cardio drumming.[3][4]
Inpopular music and jazz, "drums" usually refers to a drum kit or a set of drums (with some cymbals, or in the case of harder rock music genres, many cymbals), and "drummer" to the person who plays them.
Drums acquired even divine status in places such as Burundi, where the karyenda was a symbol of the power of the king.
The shell almost always has a circular opening over which the drumhead is stretched, but the shape of the remainder of the shell varies widely. In the Western musical tradition, the most usual shape is a cylinder, although timpani, for example, use bowl-shaped shells.[1] Other shapes include a frame design (tar, Bodhrán), truncated cones (bongo drums, Ashiko), goblet shaped (djembe), and joined truncated cones (talking drum).
A drum contains cylindrical shells can be open at one end (as is the case with timbales), or can have two drum heads, one head on each end. Single-headed drums typically consist of a skin stretched over an enclosed space, or over one of the ends of a hollow vessel. Drums with two heads covering both ends of a cylindrical shell often have a small hole somewhat halfway between the two heads; the shell forms a resonating chamber for the resulting sound. Exceptions include the African slit drum, also known as a log drum as it is made from a hollowed-out tree trunk, and the Caribbean steel drum, made from a metal barrel. Drums with two heads can also have a set of wires, called snares, held across the bottom head, top head, or both heads, hence the name snare drum.[1] On some drums with two heads, a hole or bass reflex port may be cut or installed onto one head, as with some 2010s era bass drums in rock music.
On modern band and orchestral drums, the drumhead is placed over the opening of the drum, which in turn is held onto the shell by a "counterhoop" (or "rim"), which is then held by means of a number of tuning screws called "tension rods" that screw into lugs placed evenly around the circumference. The head's tension can be adjusted by loosening or tightening the rods. Many such drums have six to ten tension rods. The sound of a drum depends on many variables—including shape, shell size and thickness, shell materials, counterhoop material, drumhead material, drumhead tension, drum position, location, and striking velocity and angle.[1]
Prior to the invention of tension rods, drum skins were attached and tuned by rope systems—as on the Djembe—or pegs and ropes such as on Ewe drums.[5] These methods are rarely used today, though sometimes appear on regimental marching band snare drums.[1] The head of a talking drum, for example, can be temporarily tightened by squeezing the ropes that connect the top and bottom heads. Similarly, the tabla is tuned by hammering a disc held in place around the drum by ropes stretching from the top to bottom head. Orchestral timpani can be quickly tuned to precise pitches by using a foot pedal.

Several factors determine the sound a drum produces, including the type, shape and construction of the drum shell, the type of drum heads it has, and the tension of these drumheads. Different drum sounds have different uses in music. For example, the modern Tom-tom drum. A jazz drummer may want drums that are high pitched, resonant and quiet whereas a rock drummer may prefer drums that are loud, dry and low-pitched.
The drum head has the most effect on how a drum sounds. Each type of drum head serves its own musical purpose and has its own unique sound. Double-ply drumheads dampen high frequency harmonics because they are heavier and they are suited to heavy playing.[6] Drum heads with a white, textured coating on them muffle the overtones of the drum head slightly, producing a less diverse pitch. Drum heads with central silver or black dots tend to muffle the overtones even more, while drum heads with perimeter sound rings mostly eliminate overtones. Some jazz drummers avoid using thick drum heads, preferring single ply drum heads or drum heads with no muffling. Rock drummers often prefer the thicker or coated drum heads.
The second biggest factor that affects drum sound is head tension against the shell. When the hoop is placed around the drum head and shell and tightened down with tension rods, the tension of the head can be adjusted. When the tension is increased, the amplitude of the sound is reduced and the frequency is increased, making the pitch higher and the volume lower.
The type of shell also affects the sound of a drum. Because the vibrations resonate in the shell of the drum, the shell can be used to increase the volume and to manipulate the type of sound produced. The larger the diameter of the shell, the lower the pitch. The larger the depth of the drum, the louder the volume. Shell thickness also determines the volume of drums. Thicker shells produce louder drums. Mahogany raises the frequency of low pitches and keeps higher frequencies at about the same speed. When choosing a set of shells, a jazz drummer may want smaller maple shells, while a rock drummer may want larger birch shells.

Drums made with alligator skins have been found in Neolithic cultures located in China, dating to a period of 5500–2350 BC. In literary records, drums manifested shamanistic characteristics and were often used in ritual ceremonies.[7]
The bronze Dong Son drum was fabricated by the Bronze Age Dong Son culture of northern Vietnam. They include the ornate Ngoc Lu drum.
Macaque monkeys drum objects in a rhythmic way to show social dominance and this has been shown to be processed in a similar way in their brains to vocalizations, suggesting an evolutionary origin to drumming as part of social communication.[8] Other primates including gorillas make drumming sounds by chest beating or hand clapping,[9][10] and rodents such as kangaroo rats also make similar sounds using their paws on the ground.[11]
Drums are used not only for their musical qualities, but also as a means of communication over great distances. The talking drums of Africa are used to imitate the tone patterns of spoken language. Throughout Sri Lankan history drums have been used for communication between the state and the community, and Sri Lankan drums have a history stretching back over 2500 years.

Drumming may be a purposeful expression of emotion for entertainment, spiritualism and communication. Many cultures practice drumming as a spiritual or religious passage and interpret drummed rhythm similarly to spoken language or prayer. Drumming has developed over millennia to be a powerful art form. Drumming is commonly viewed as the root of music and is sometimes performed as a kinesthetic dance. As a discipline, drumming concentrates on training the body to punctuate, convey and interpret musical rhythmic intention to an audience and to the performer.
Chinese troops used tàigǔ drums to motivate troops, to help set a marching pace, and to call out orders or announcements. For example, during a war between Qi and Lu in 684 BC, the effect of drum on soldiers' morale is employed to change the result of a major battle. Fife-and-drum corps of Swiss mercenary foot soldiers also used drums. They used an early version of the snare drum carried over the player's right shoulder, suspended by a strap (typically played with one hand using traditional grip). It is to this instrument that the English word "drum" was first used. Similarly, during the English Civil War rope-tension drums would be carried by junior officers as a means to relay commands from senior officers over the noise of battle. These were also hung over the shoulder of the drummer and typically played with two drum sticks. Different regiments and companies would have distinctive and unique drum beats only they recognized. In the mid-19th century, the Scottish military started incorporating pipe bands into their Highland regiments.[12]
During pre-Columbian warfare, Aztec nations were known to have used drums to send signals to the battling warriors. The Nahuatl word for drum is roughly translated as huehuetl.[13]
The Rig Veda, one of the oldest religious scriptures in the world, contains several references to the use of the Dundhubi (war drum). Arya tribes charged into battle to the beating of the war drum and chanting of a hymn that appears in Book VI of the Rig Veda and also the Atharva Veda.[14] The dundhuhi was considered sacred and to capture one in battle would signal defeat of the enemy.[15]


{{cite book}}: |website= ignored (help)
|
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
List of percussion instruments | |||||
| Pitched percussion |
| ||||
| Unpitched percussion |
| ||||
| Electronic percussion |
| ||||
| Percussion groupings |
| ||||
| Other |
| ||||
| National |
|
|---|---|
| Other |
|