J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 S e e a l s o
2 A d d i t i o n a l i m a g e s
3 R e f e r e n c e s
4 E x t e r n a l l i n k s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
L a t e r a l e p i c o n d y l e o f t h e h u m e r u s
1 1 l a n g u a g e s
● ا ل ع ر ب ي ة ● C a t a l à ● E s p a ñ o l ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● G a l e g o ● M a g y a r ● N o r s k b o k m å l ● P o r t u g u ê s ● R o m â n ă ● ไ ท ย
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
I n o t h e r p r o j e c t s
● W i k i m e d i a C o m m o n s
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
( R e d i r e c t e d f r o m E c t e p i c o n d y l e )
The lateral epicondyle of the humerus is a large, tuberculated eminence, curved a little forward, and giving attachment to the radial collateral ligament of the elbow joint, and to a tendon common to the origin of the supinator and some of the extensor muscles. Specifically, these extensor muscles include the anconeus muscle , the supinator , extensor carpi radialis brevis , extensor digitorum , extensor digiti minimi , and extensor carpi ulnaris .[1] In birds , where the arm is somewhat rotated compared to other tetrapods , it is termed dorsal epicondyle of the humerus . In comparative anatomy, the term ectepicondyle is sometimes used.[2]
A common injury associated with the lateral epicondyle of the humerus is lateral epicondylitis also known as tennis elbow . Repetitive overuse of the forearm, as seen in tennis or other sports, can result in inflammation of "the tendons that join the forearm muscles on the outside of the elbow. The forearm muscles and tendons become damaged from overuse. This leads to pain and tenderness on the outside of the elbow."[3]
See also
[ edit ]
Additional images
[ edit ]
Right lateral epicondyle colored in red
Left humerus. Anterior view.
Plan of ossification of the humerus.
Posterior surface of the forearm. Superficial muscles.
Posterior surface of the forearm. Deep muscles.
References
[ edit ]
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 212 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
^ "Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)" . OrthoInfo . American Academy of Orthpedic Surgeons. Retrieved 9 December 2013 .
External links
[ edit ]
t
e
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Lateral_epicondyle_of_the_humerus&oldid=1221883591 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● W i k i p e d i a a r t i c l e s i n c o r p o r a t i n g t e x t f r o m t h e 2 0 t h e d i t i o n o f G r a y ' s A n a t o m y ( 1 9 1 8 ) ● U p p e r l i m b a n a t o m y ● H u m e r u s ● M u s c u l o s k e l e t a l s y s t e m s t u b s H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n m a t c h e s W i k i d a t a ● A r t i c l e s w i t h T A 9 8 i d e n t i f i e r s ● A l l s t u b a r t i c l e s
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 2 M a y 2 0 2 4 , a t 1 5 : 2 3 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w


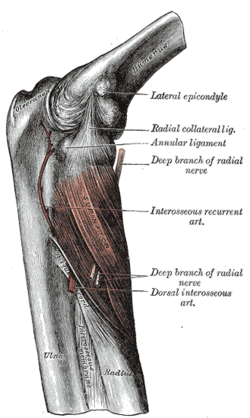
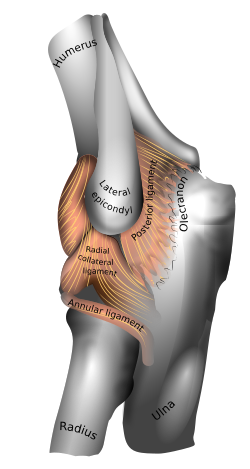
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 212 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 212 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)