

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Petzval field curvature" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. Please help improve ittomake it understandable to non-experts, without removing the technical details. (May 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message)
|
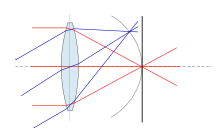
Petzval field curvature, named for Joseph Petzval,[1] describes the optical aberration in which a flat object normal to the optical axis (or a non-flat object past the hyperfocal distance) cannot be brought properly into focus on a flat image plane.[citation needed] Field curvature can be corrected with the use of a field flattener, designs can also incorporate a curved focal plane like in the case of the human eye in order to improve image quality at the focal surface.

Consider an "ideal" single-element lens system for which all planar wave fronts are focused to a point at distance f from the lens. Placing this lens the distance f from a flat image sensor, image points near the optical axis will be in perfect focus, but rays off axis will come into focus before the image sensor, dropping off by the cosine of the angle they make with the optical axis. This is less of a problem when the imaging surface is spherical, as in the human eye.
Most current photographic lenses are designed to minimize field curvature, and so effectively have a focal length that increases with ray angle. Lenses of short focal lengths (ultra wide, wide and normal) below 50 mm typically suffer more from field curvature. Telephoto lenses typically have very little or no visible field curvature.[2] The Petzval lens is one design which has significant field curvature; images taken with the lens are very sharp in the centre, but at greater angles the image is out of focus. Film cameras may be able to bend their image planes to compensate, particularly when the lens is fixed and known. This also includes plate film, which could still be bent slightly. Digital sensors are difficult to bend, although experimental products have been produced.[3] By 2016 the only consumer cameras featuring curved sensors were "selfie" Sony Cybershot KW-1 and KW-11.[citation needed] Large mosaics of sensors (necessary anyway due to limited chip sizes) can be shaped to simulate a bend over larger scales.[citation needed]
The Petzval field curvature is equal to the Petzval sum over an optical system,

where 
The primary way to control this aberration is by inserting further optical elements which counteract the curved focal plane off axis. This is especially important for wide-angle lens designs since this aberration is an exponential function of angle off axis
Ironically, the two groups in a Petzval portrait lens are primarily intended to control spherical aberration and coma, but actually make field curvature worse. This tradeoff was desirable because for a long focus lens better correction of spherical aberration and coma permits a faster aperture setting, which is more important than any defect of field curvature since long focus lenses have a narrow angle of view.
Anaperture stop (iris) reduces the effect of field curvature by reducing the circle of confusion, but does not actually affect the curvature of the focal plane. Using a small aperture to limit the effect of field curvature greatly decreases the light collecting power of the lens.[5]