

The interferometric visibility (also known as interference visibility and fringe visibility, or just visibility when in context) is a measure of the contrastofinterference in any system subject to wave superposition. Examples include as optics, quantum mechanics, water waves, sound waves, or electrical signals. Visibility is defined as the ratio of the amplitude of the interference pattern to the sum of the powers of the individual waves. The interferometric visibility gives a practical way to measure the coherence of two waves (or one wave with itself). A theoretical definition of the coherence is given by the degree of coherence, using the notion of correlation.
Generally, two or more waves are superimposed and as the phase difference between them varies, the powerorintensity (probability or population in quantum mechanics) of the resulting wave oscillates, forming an interference pattern. The pointwise definition may be expanded to a visibility function varying over time or space. For example, the phase difference varies as a function of space in a two-slit experiment. Alternately, the phase difference may be manually controlled by the operator, for example by adjusting a vernier knob in an interferometer.
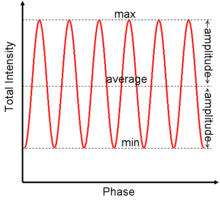
In linear optical interferometers[clarification needed] (like the Mach–Zehnder interferometer, Michelson interferometer, and Sagnac interferometer), interference manifests itself as intensity oscillations over time or space, also called fringes. Under these circumstances, the interferometric visibility is also known as the "Michelson visibility" [1] or the "fringe visibility." For this type of interference, the sum of the intensities (powers) of the two interfering waves equals the average intensity over a given time or space domain. The visibility is written as:[2]

in terms of the amplitude envelope of the oscillating intensity and the average intensity:


So it can be rewritten as:[3]

where Imax is the maximum intensity of the oscillations and Imin the minimum intensity of the oscillations.


If the two optical fields are ideally monochromatic (consist of only single wavelength) point sources of the same polarization, then the predicted visibility will be

where 




Since the Schrödinger equation is a wave equation and all objects can be considered waves in quantum mechanics, interference is ubiquitous. Some examples: Bose–Einstein condensates can exhibit interference fringes. Atomic populations show interference in a Ramsey interferometer. Photons, atoms, electrons, neutrons, and molecules have exhibited interference in double-slit interferometers.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)