

| IQ calmodulin-binding motif | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
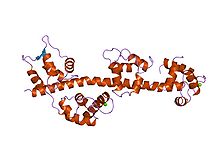
Structure of the regulatory domain of scallop myosin at 2 A resolution.[1]
| |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | IQ | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00612 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000048 | ||||||||||
| SMART | SM00015 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PS50096 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1wdc / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The IQ calmodulin-binding motif is an amino acid sequence motif containing the following sequence:
The term "IQ" refers to the first two amino acids of the motif: isoleucine (commonly) and glutamine (invariably).
Calmodulin (CaM) is recognized as a major calcium (Ca2+) sensor and orchestrator of regulatory events through its interaction with a diverse group of cellular proteins. Three classes of recognition motifs exist for many of the known CaM binding proteins; the IQ motif as a consensus for Ca2+-independent binding and two related motifs for Ca2+-dependent binding, termed 1-14 and 1-5-10 based on the position of conserved hydrophobic residues.[2]
The regulatory domain of scallop myosin is a three-chain protein complex that switches on this motor in response to Ca2+ binding. Side-chain interactions link the two light chains in tandem to adjacent segments of the heavy chain bearing the IQ-sequence motif. The Ca2+-binding site is a novel EF hand motif on the essential light chain and is stabilized by linkages involving the heavy chain and both light chains, accounting for the requirement of all three chains for Ca2+binding and regulation in the intact myosin molecule.[3]