J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 N a m e
2 R e f e r e n c e s
3 E x t e r n a l l i n k s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
I n t e r l o b u l a r a r t e r i e s
8 l a n g u a g e s
● ا ل ع ر ب ي ة ● B o s a n s k i ● C a t a l à ● E s p a ñ o l ● E u s k a r a ● F r a n ç a i s ● R o m â n ă ● С р п с к и / s r p s k i
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
( R e d i r e c t e d f r o m I n t e r l o b u l a r )
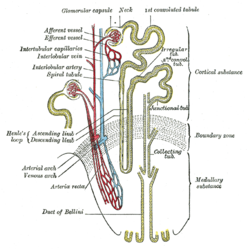
Cortical radial arteries , formerly known as interlobular arteries ,[1] renal blood vessels given off at right angles from the side of the arcuate arteries looking toward the cortical substance . The interlobular arteries pass directly outward between the medullary rays to reach the fibrous tunic, where they end in the capillary network of this part.
These vessels do not anastomose with each other, but form end-arteries .
In their outward course, they give off lateral branches, which are the afferent arterioles that supply the renal corpuscles . The afferent arterioles, then, enter Bowman's capsule and end in the glomerulus .
From each glomerulus, the corresponding efferent arteriole arises and then exits the capsule near the point where the afferent arteriole enters. Distally , efferent arterioles branch out to form dense plexuses (i.e., capillary beds ) around their adjacent renal tubules . For cortical nephrons , a single network of capillaries, known as the peritubular capillaries , surrounds the entire renal tubule, whereas for juxtamedullary nephrons , the peritubular capillaries surround only the proximal and distal convoluted tubules , while another network branching from the efferent arteriole, known as the straight arterioles of kidney , surrounds the nephron loop (of Henle ).
Lote refers to them as "cortical radial arteries (formerly called inter-lobular arteries) "[1]
Mescher et al refer to them as "interlobular arteries (or cortical radial arteries) "[2]
References [ edit ]
^ a b Lote, Christopher J. (2012). Principles of Renal Physiology, 5th edition . Springer. p. 28.
^ Mescher, Anthony L. (2016). Junqueira's Basic Histology, 14th edition . Lange. p. 394.
External links [ edit ]
Histology image: 16015loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Urinary System: kidney, H&E, interlobular artery and vein"
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Interlobular_arteries&oldid=1192859903 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● W i k i p e d i a a r t i c l e s i n c o r p o r a t i n g t e x t f r o m t h e 2 0 t h e d i t i o n o f G r a y ' s A n a t o m y ( 1 9 1 8 ) ● K i d n e y a n a t o m y H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● A n a t o m y N A V i n f o b o x w i t h u s e o f o t h e r N A V p a r a m e t e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h T A 9 8 i d e n t i f i e r s
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 3 1 D e c e m b e r 2 0 2 3 , a t 1 9 : 0 7 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w