

435–534
565–774
774–885
Frankish (as part of the Carolingian Empire)
885–961
Germanic (as part of the Holy Roman Empire)
961–1801
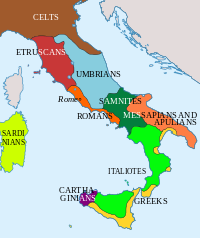

The Italiotes (Greek: Ἰταλιῶται, Italiōtai) were the pre-Roman Greek-speaking inhabitants of the Italian Peninsula, between Naples and Calabria.[citation needed]
Greek colonisation of the coastal areas of southern Italy and Sicily started in the 8th century BC and, by the time of the Roman ascendance, the area was so extensively hellenized that Romans called it Magna Graecia, that is "Greater Greece".
The Latin alphabet is a derivative of the Western Greek alphabet used by these settlers, and was picked up and adopted and modified first by the Etruscans and then by the Romans.[citation needed]
Kingdoms
Artists & scholars
Others
By culture
Arts and science
Sacred places
Structures
Black Sea
basin
South
coast