


Passenger load factor, or load factor, measures the capacity utilizationofpublic transport services like airlines, passenger railways, and intercity bus services. It is generally used to assess how efficiently a transport provider fills seats and generates fare revenue.
According to the International Air Transport Association, the worldwide load factor for the passenger airline industry during 2015 was 79.7%.[1]
Passenger load factor is an important parameter for the assessment of the performance of any transport system. Almost all transport systems have high fixed costs, and these costs can only be recovered through selling tickets.[2] Airlines often calculate a load factor at which the airline will break even; this is called the break-even load factor.[3] At a load factor lower than the break even level, the airline will lose money, and above will record a profit.
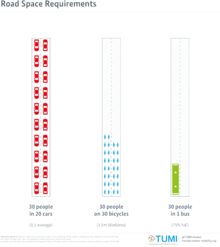
The environmental performance of any transport mode improves as the load factor increases. The weight of passengers is normally a small part of the total weight of any transport vehicle, so increasing the number of passengers changes the emissions and fuel consumption to only a small degree. As a vehicle is more highly loaded, the fuel consumed per passenger drops, and fully loaded transport vehicles can be very fuel efficient.
Very heavy loading of a transport vehicle is described as a crush load. Crush loading is a very high level of loading where passengers are crushed against one another. Commenting in May 2017 on the United Express Flight 3411 incident, in which a passenger was forcibly removed, investor Warren Buffett said that passenger demand for cheap flights was resulting in high load factors, resulting in "a fair amount of discomfort."[4]
Specifically, the load factor is the dimensionless ratio of passenger-kilometres travelled to seat-kilometres available. For example, say that on a particular day an airline makes 5 scheduled flights, each of which travels 200 kilometers and has 100 seats, and sells 60 tickets for each flight. To calculate its load factor:

Thus, during that day the airline flew 60,000 passenger-kilometres and 100,000 seat-kilometres, for an overall load factor of 60% (0.6).
|
| ||
|---|---|---|
| Chassis |
| |
| Roadway |
| |
| Uses |
| |
| Power |
| |
| Manufacturing |
| |
| ||