

| Structural formula | 
|

|

|
|
| Name | Fluoromethane Methyl fluoride |
Chloromethane Methyl chloride |
Bromomethane Methyl bromide |
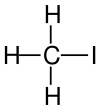
Iodomethane Methyl iodide |
| Melting point | −137,8 °C[1] | −97,4 °C[2] | −93,7 °C[3] | −66 °C[4] |
| Boiling point | −78,4 °C[1] | −23,8 °C[2] | 4,0 °C[3] | 42 °C[4] |
| Space-filling model | 
|

|

|

|
The monohalomethanes are organic compounds in which a hydrogen atom in methane is replaced by a halogen. They belong to the haloalkanes or to the subgroup of halomethanes.
The four common[a] members are fluoromethane, chloromethane, bromomethane and iodomethane.
Historical name for this group is methyl halides; it's still widely used. The compounds of this class are often described as CH3X or MeX (X - any halogen, Me - methyl group).
There are analogs with more than one hydrogen atom in methane is replaced by a halogen:
Analogs with carbon atom replaced with a heavier group 14 element are also known: