

| Phalen maneuver | |
|---|---|
Phalen's maneuver
| |
| Purpose | test carpal tunnel syndrome |
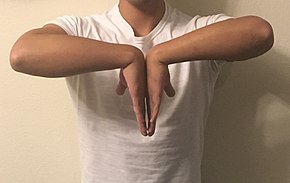
Phalen's maneuver is a diagnostic test for carpal tunnel syndrome[1] by an American orthopedist named George S. Phalen.[2]
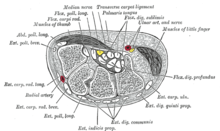
The patient is asked to hold their wrists in complete and forced flexion (pushing the dorsal surfaces of both hands together) for 30–60 seconds. The lumbricals attach in part to the flexor digitorum profundus tendons. As the wrists flex, the flexor digitorum profundus contracts in a proximal direction, drawing the lumbricals along with it. In some individuals, the lumbricals can be "dragged" into the carpal tunnel with flexor digitorum profundus contraction. As such, Phalen's maneuver can moderately increase the pressure in the carpal tunnel via this mass effect, pinching the median nerve between the proximal edge of the transverse carpal ligament and the anterior border of the distal end of the radius. By compressing the median nerve within the carpal tunnel, characteristic symptoms (such as burning, tingling or numb sensation over the thumb, index, middle and ring fingers) convey a positive test result and suggest carpal tunnel syndrome. Because not all individuals will draw the lumbricals into the carpal tunnel with this maneuver, this test cannot be perfectly sensitive or specific for carpal tunnel syndrome.[3]
In studies of diagnostic accuracy, the sensitivity of the Phalen's maneuver ranged from 51% to 91% and its specificity from 33% to 88%.[citation needed]

This test is performed by having the patient maintain full wrist and finger extension for two minutes. The reverse Phalen's test significantly increases pressure in the carpal tunnel within 10 seconds of the change in wrist posture and the carpal tunnel pressure has the tendency to increase throughout the test's duration. In contrast, the change in carpal tunnel pressure noted in the standard Phalen's test is modest and plateaus after 20 to 30 seconds.
The average pressure change for Phalen's test at one and two minutes was only 4 mm Hg.[citation needed] The average pressure changes in the carpal tunnel for the reverse Phalen's test were 34 mm Hg at one minute into the test and 42 mm Hg at the two-minute point.[citation needed]
The extended wrist posture significantly changes the pressure within the carpal tunnel and may be more useful as a provocative examination maneuver. Reverse Phalen's maneuver results in a significantly higher intracarpal canal hydrostatic pressure as compared to a traditional Phalen's.[4] This is thought to add to the sensitivity of conventional screening methods.
Phalen's maneuver is more sensitive than Tinel's sign.[5]
|
Signs and symptoms relating to the nervous system
| |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Central nervous system |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Peripheral nervous system |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
Musculoskeletal examination
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leg |
| ||||||||
| Arm |
| ||||||||
| Spine |
| ||||||||
| Other |
| ||||||||