

Inautomobile design, a rear-engine design layout places the engine at the rear of the vehicle. The center of gravity of the engine itself is behind the rear axle. This is not to be confused with the center of gravity of the whole vehicle, as an imbalance of such proportions would make it impossible to keep the front wheels on the ground.
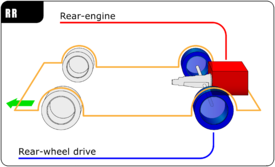
Rear-engined vehicles almost always have a rear-wheel drive car layout, but some are four wheel drive. This layout has the following features:
This layout was once popular in small, inexpensive cars and light commercial vehicles. Today most car makers have abandoned the layout although it does continue in some expensive cars,[3] like the Porsche 911. It is also used in some racing car applications,[4] low-floor buses, some Type-D school buses, and microcars such as the Smart Fortwo. Some electric cars feature both rear and front motors, to drive all four wheels.[5]
