

| Mastoid antrum | |
|---|---|
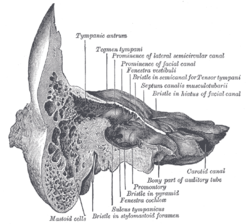
Coronal section of right temporal bone. ("Tympanic antrum" labeled at upper left.)
| |
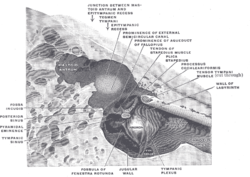
The medial wall and part of the posterior and anterior walls of the right tympanic cavity, lateral view. ("Mastoid antrum" labeled at upper left, in dark circle.)
| |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | antrum mastoideum |
| TA98 | A15.3.02.028 |
| TA2 | 645 |
| FMA | 55711 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The mastoid antrum (tympanic antrum, antrum mastoideum, Valsalva's antrum) is an air space in the petrous portion of the temporal bone, communicating posteriorly with the mastoid cells and anteriorly with the epitympanic recess of the middle ear via the aditus to mastoid antrum (entrance to the mastoid antrum). These air spaces function as sound receptors, provide voice resonance, act as acoustic insulation and dissipation, provide protection from physical damage and reduce the mass of the cranium.[citation needed] The roof is formed by the tegmen antri which is a continuation of the tegmen tympani and separates it from the middle cranial fossa. The lateral wall of the antrum is formed by a plate of bone which is an average of 1.5 cm in adults. The mastoid air cell system is a major contributor to middle ear inflammatory diseases.[1]
|
Neurocranium of the skull
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Occipital |
| ||||||||||
| Parietal |
| ||||||||||
| Frontal |
| ||||||||||
| Temporal |
| ||||||||||
| Sphenoid |
| ||||||||||
| Ethmoid |
| ||||||||||