魚の鱗
表示
この項目﹁魚の鱗﹂は翻訳されたばかりのものです。不自然あるいは曖昧な表現などが含まれる可能性があり、このままでは読みづらいかもしれません。︵原文‥en:Fish scale18:37, 1 December 2020︶
修正、加筆に協力し、現在の表現をより自然な表現にして下さる方を求めています。ノートページや履歴も参照してください。︵2020年12月︶ |

魚の鱗︵さかなのうろこ 英:Fish scale︶は、魚類の真皮から生じた骨質の保護小片である[1]。大部分の魚類の皮膚は保護的な鱗で覆われ、これが反射と色彩を使った効果的なカモフラージュを可能にしたり、流体力学上の利点にもなっている。
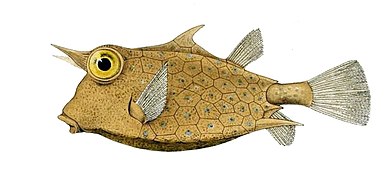
ヘコアユやハコフグ科などの魚にある強くて硬い装甲板から、ウナギ科やアンコウ目などの魚では微小あるいは無いものまで、鱗は︵種によって︶大きさ、形状、構造、範囲が大きく異なる。鱗の形態学 (生物学)は、その由来となる魚の種を識別するのに使用されてもいる。
大部分の硬骨魚類は、円鱗か櫛鱗またはガノイン鱗で覆われている。軟骨魚類は楯鱗で覆われている。一部の種は稜鱗で覆われており、これ以外では外皮を覆う鱗が一部または全部無いものもいる。
魚類の鱗は魚の外皮系の一部で、真皮の中皮層から生成され、ここが爬虫類の鱗︵表皮起源︶とは異なる点である[2][3]。哺乳類の歯や毛髪の発達に関わるのと同じ遺伝子が、鱗の発達に関与している。軟骨魚の楯鱗は皮歯とも呼ばれ、脊椎動物の歯と構造的に相同する。大部分の魚類は、細菌、真菌、ウイルスなどの病原体から身を守ったり泳ぐ際の表面抵抗を下げることが可能な粘液またはゼリー状の層で覆われている。
歯鱗上綱の鱗
[編集]
化石魚の最も豊富な形態となる歯鱗上綱[4]の骨鱗はよく理解されている。この鱗は生物の生涯にわたって形成および脱皮し、死後すぐに剥がれていった[5]。
骨は、力学的損傷に耐性があり比較的化石になりやすい組織で、内部詳細を保っていることも多く、これが鱗の組織学や成長の詳細な研究を可能にしている。この鱗には象牙質で構成された成長しない"クラウン"[注釈 1]が含まれ、たまに装飾的なエナメロイドの上面とアスピジンの基底がある[6]。その成長する基底は無細胞の骨質で作られており、片側には固定するためのアンカーレッジ構造[注釈 2]を発達させる魚もいた[7]。
ただし、鱗形態学を単独で使用して種を区別するには、幾つかの落とし穴がある。個々の生物内でも鱗の形状は胴部によって大きく異なり、中間形態が異なる部位で現れ[8]、さらに悪いことに鱗の形態が一つの領域でも異なる場合すらある。加えて混乱を招くこととして、鱗の形態はタクソンに固有のものではなく、異なる二種の同一部位では区別不能な場合もある[9]。
歯鱗上綱の形態学と組織学は、その多様性を定量化したり種間を区別するための主要な手段を提供してはいるものの、そうした収斂の形質を用いると最終的には誤謬が発生しやすくなる。にもかかわらず、鱗の形態学と組織学に基づいて3グループに構成する枠組みが提案されている[10]。現代のサメ種との比較で、歯鱗上綱の鱗が現代の軟骨魚の鱗と機能的に似通ったものだという事が示された[11]。
コズミン鱗
[編集]
コズミン鱗は、初期のハイギョ︵肺魚下綱︶数種類を含む古代の肉鰭類と、現生するシーラカンス目の変成態を含む総鰭下綱でのみ発見されている︵後述の板状鱗を参照︶。これは恐らく楯鱗の融合から派生したものとされる。鱗の内側部分はイソペジンと呼ばれる稠密なラメラ構造骨でできている。この上に血管を供給する海綿状または網目状の骨層があり、これに続いてビトロデンチン︵というエナメル層物質︶の表被膜に覆われたコズミンと呼ばれる象牙質に似た複雑な層がある。その上面はケラチンである。コズミン鱗はラメラ骨層の成長を通じてサイズが増大する[12]。
板状鱗
[編集]
板状鱗は、イソペジンと呼ばれる稠密なラメラ構造コラーゲン骨の層で構成された薄い覆瓦構造の鱗であり、その上には通常︵エウステノプテロンのように︶骨で構成された結節層がある。最初の肉鰭類に存在していた象牙質層は︵現生種シーラカンスのように︶通常だと減っているか、︵現生種ハイギョやデボン紀のエウステノプテロンのように︶全く存在しない[13]。板状鱗は、魚類の進化過程で数回出現している。この鱗は一部の肉鰭類︵現生する全てのハイギョや絶滅した一部のハイギョ、およびコズミン欠乏でコズミン鱗を変容させたシーラカンス︶に見られる。その鱗はまた、エウステノプテロン、アミア科、真骨魚類のような扇鰭亜綱の幾つかに存在しており、それらの円鱗と櫛鱗は石灰化が最も少ない板状鱗の典型である。
ゼブラフィッシュの板状鱗は骨の石灰化プロセスを研究する目的で実験室にて活用されており、生体外で培養︵保管︶することが可能である[14][15]。
ガノイン鱗
[編集]

ガノイン鱗はチョウザメ目、ヘラチョウザメ、ガー目、アミア・カルヴァ、ポリプテルスで見られる。それはコズミン鱗から派生したもので、鋸歯状の先端であることも多い。この鱗はコズミンの代わりに硬いエナメルのような象牙質の層と、ビトロデンチンの代わりにガノインと呼ばれる無機骨塩の層とで覆われている。
ガノインはガノイン鱗の特徴的な成分である。それはガラス状で、鱗を覆う多層化されたミネラル化組織であることも多く、一部の条鰭類︵ガー、ポリプテルス、シーラカンスなど︶[16][17]では頭蓋骨や鰭条をも覆っていたりする[18]。それは棒状のアパタイト結晶で構成されている[19]。ガノインは、例えば条鰭類のステムグループであるケイロレピスなどの鱗に見られる古代の条鰭類の特徴である[17]。条鰭類の共有派生形質上の特徴だと見なされることも多いが、ガノインないしガノイン状組織は絶滅した棘魚類でも発見されている[17]。ガノインは、脊椎動物における歯のエナメル質と相同性があると示唆されており[18]、エナメル質の一種とさえ考えられている[19]。
 |
絶滅した石炭紀の魚類Amblypterus striatusのガノイン鱗。(a)は鱗4枚の外面を示したもので(b)は鱗2枚の内面を示したもの。アンブリプテルス科の菱形をしたガノイン鱗はそれぞれ内側の一端に隆起があって、次の鱗の窪みにちょうど収まる釘の役目を果たすように作られており、言うなれば家の屋根に瓦を釘打ち固定する方法に似ている。 | 
|
大半のガノイン鱗は菱形で、隆起と凹みの組み合わせで繋がっている。一般的にこの鱗は厚くて、他の鱗のように積み重なるというよりもジグソーパズルのように組み合わさっていく[20]。この方法でもガノイン鱗は殆ど貫通を許さず、捕食に対する優秀な保護である。

チョウザメ科では側面と背中に沿って鱗が非常に大型化した硬鱗があり、アミア・カルヴァでは鱗が円鱗に似た厚さへと大幅に小型化している。
-
アリゲーターガーのガノイン鱗から作られたイアリング
-
ガノイン鱗がある原始的な条鰭類の化石
-
化石になったレピドテスのガノイン鱗。約1.3億年前
アメリカ先住民とカリブ海域の人々は、アリゲーターガーの頑強なガノイン鱗を矢の先端部や胸当てに使っていた。現在ではアクセサリーがこれらの鱗から作られている[21]。
葉状鱗
[編集]
葉状鱗︵骨鱗︶は、より高次の硬骨魚類︵条鰭類の派生系統群︶に見られる。この鱗の外側部分は骨稜と共に扇状に広がり、内側部分は繊維状結合組織と十字交差する。葉状鱗は、他の鱗よりも薄く半透明で、硬化したエナメル状の層や象牙質層が欠落している。ガノイン鱗とは異なり、魚が成長するにつれてさらなる鱗が同心円状の層に追加される[22]。
葉状鱗は頭から尾への配置構成で屋根瓦のように重なり、コズミン鱗やガノイン鱗よりも柔軟である。この配置が体表全体に水の滑らかな流れをつくりあげ、流体抗力を減らす[23]。一部の葉状鱗では年輪と呼ばれる不均一な季節的成長の輪が見られ、この輪は魚類の年齢査定に用いられている[24]。
葉状鱗には、円鱗と櫛鱗という2つの形状がある。
円鱗
[編集]円鱗は滑らかな質感で、外側の端部や縁でも滑らかさが均一である。この鱗はサケやコイといった軟条鰭の魚で最も一般的である。

|

|
| アジアアロワナには肋骨上にモザイク配置された大きな円鱗がある(左)。鱗自体は繊細な網目模様となっている(右)[25][26]。 | |
円鱗
コイの円鱗は外側端部(画像だと頂部)が滑らか
コイに似た Poropuntius hugueniniという魚には、触ると滑らかな円鱗がある
| 様々な魚の円鱗(一般的にはサケやコイで見られる) |
櫛鱗
[編集]
櫛鱗は円鱗に似ているが、外側または後部の縁に沿ってcteniiと呼ばれるギザギザ又は小棘[27]がある。これら小棘があるため、この鱗はざらついた質感である。これらは一般的にスズキ目のように鰭棘のある魚に見られる。この鱗には殆ど骨が含まれず、水酸アパタイトと炭酸カルシウムを含む表層と、主にコラーゲンからなる深層とで構成されている。他種の鱗でのエナメル質が、表面上の隆起およびcteniiに縮減したものとなっている。

|

|
| 頭が大きく尾が細い深海魚Cetonurus crassicepsから採取された例のように、小棘の大きさは部位で異なることもありうる | |


| 様々な魚の櫛鱗(一般的にはスズキ目で見られる) |
櫛鱗は他の表皮構造と同じくプラコード[注釈 3]から派生したもので、独特の細胞分化がそれらを外皮系から生じる他の構造とは別物にさせている[30]。その発達は魚の側線に沿って尾鰭付近で始まる[31]。発達プロセスは表皮と真皮の間に線維芽細胞が蓄積して始まる[30]。コラーゲン線維は真皮層で組織化を始め、それがミネラル化の開始をもたらす[30]。鱗の周囲がまず成長し、重なり合う層が一緒にミネラル化する際に厚さ︵の成長︶が続く[30]。
櫛鱗はさらに3種類に分類可能である。
●鱗の縁にギザギザと突起が生じるもの(Crenate)。
●鱗全体に小棘が生じるもの(spinoid)。
●鱗上にある小棘が鮮明な構造のもの(True ctenoid)。
大部分の硬骨魚類は櫛鱗である。一部のカレイ目では、目のある側が櫛鱗で目のない側が円鱗となっていたり、オスが櫛鱗でメスが円鱗という種もいる。
反射
[編集]


多くの真骨魚類は、小さな鏡のように機能して銀色のガラス光沢を与える反射率の高い鱗で覆われている。銀色を介する反射は特に水深100m以内に生息する海生魚で広く支配的である。透明効果は、魚の体躯を高反射させて銀色ががることで成し遂げられる。海中半ばの深さでは上から光が来るので、垂直を向いた鏡︵反射体︶が魚影を横から見えないようにしてしまう[32]。
ムネエソ科は非常に平たく、胴部は横(幅)の厚みがほんの数mmでアルミ箔を思わせるほど銀色がかっている。その鏡は、構造色で使われるのと同様の顕微構造で構成されている。5-10のグアニン結晶の重なりが波長の約1/4間隔で配置されており、これが干渉してほぼ100%の反射を達成する。ムネエソ科が生息する深海では波長500ナノメートルの青色光だけが降り注ぎ、また反射させる必要があるため、125ナノメートル間隔の鏡が良いカモフラージュを作り出す[32]。
上記のように海生魚の大部分は銀色ががることでカモフラージュされている。浅い水域に生息するニシンなどの魚では、鏡が波長の混じったものを反射しなければならず、したがってこの魚は異なる間隔のグアニン結晶の重なりを持っている。丸みを帯びた断面の体を持つ魚との組み合わせでは、皮膚に平らに置かれた場合に鏡が水平方向に反射しなくなるので効果を得られなくなる。全体的なミラー効果は、いずれも垂直に向いている沢山の小さな反射体で成し遂げられている[32]。
こうした特性のある魚鱗は一部の化粧品で使用されており、化粧ファンデーションや口紅にきらめく効果を与えている[33]。
楯鱗
[編集]
楯鱗は、サメやエイといった軟骨魚類に見られる。﹁皮歯﹂とも呼ばれ、脊椎動物の歯と構造的に相同である[34]。楯鱗は中央の髄腔に血管が通っており、象牙質の円錐形をした層で囲まれ、その全てが真皮の上にある基底板の頂部に据えられている。最も外側の層は、主に無機エナメル状物質のビトロデンチンで構成されている。楯鱗は大きさが成長しないが、魚のサイズが大きくなるにつれて、より多くの鱗が追加されていく。
同様の鱗は Denticeps clupeoidesの頭部下にも見られる。エイではこの鱗の占める量が非常に少ない。
鮫皮
[編集]
詳細は「鮫皮」を参照
サメの皮膚はほぼ全体が小さな楯鱗で覆われている。この鱗は後ろ向きに撫でるとざらつく感触の棘による抵抗があるが、水の前方移動によって平らになると、流体力学でいう抗力や乱流を減らす小さな渦を発生させ、硬骨魚類に比べて泳ぎをより効率的かつ静粛にするもので[35]、この構造は一部の航空機にも応用されている[36]。またロータス効果を発揮することで、汚れを弾く役割も果たす[37]。
全ての皮歯は真皮内に根ざした神経や動脈を有する内部随腔で構成されており、粘液と共に皮歯を供給している[38]。皮歯には、鱗の表面から突き出たリブレット構造がある。顕微鏡下では、このリブレットが鱗から突出する鈎針や稜線状に見えたりもする。皮歯からの突起の全体的な形状はサメの種類によりまちまちだが、一般的には2つの外観にまとめられる[39]。1つ目は、稜線がサメの側線下側かつ水の流れと平行に配置されている鱗。2つ目の形状は、サメの後方部に向かって表面から巻き上がっている鈎針付きのリブレットのように見える滑らかな鱗である[39]。どちらのリブレット形状も、鮫皮から遠く離れたところで層流を強制させる乱流境界層を生み出す手伝いをする[40]。
硬骨魚類とは異なり、サメには体を取り巻くらせん網目状に配置された柔軟なコラーゲン繊維で作られた複雑な真皮のコルセット︵胴鎧︶がある。この胴鎧は外部骨格として機能し、泳ぐ筋肉に連結してエネルギーを節約する[41]。体躯にあるこれら楯鱗の位置に応じて、楯鱗は柔軟になったり受動的に屹立したりして迎角を変えることができる。またこの鱗には流れの方向に整列されたリブレットもあり、これらリブレットが渦を皮膚表面から遠ざけて押し出すことによって鮫皮に作用する抗力を減少させ、高速の偏流を抑制する[42]。
稜鱗
[編集]
稜鱗 (scute) は鱗と同じ機能を果たす。表皮から形成される魚の鱗とは異なり、稜鱗は皮膚の下血管層で形成され、表皮要素は一番上の表面のみである。真皮が生きている間に形成される稜鱗は、表面上は鱗のそれと似ている角質の外側層を生成する。
稜鱗は次の形状を取りうる。
●外部防壁のような骨板
●変形して肥厚した鱗で、しばしば稜線や棘がある
●突出した変形の︵ギザギザに大きく隆起した︶鱗で、通常は側線や尾柄や腹縁に沿っている。
マツカサウオなど一部の魚は、稜鱗で完全にまたは部分的に覆われている。アロサやツバメコノシロ科は腹部に稜鱗の列があり、これは防御目的で使用される鋭い棘のある出っ張った鱗である。一部のアジ科には側線に続く稜鱗の列が両側にある。
鱗の発達
[編集]
鱗は典型的に、魚の発達の後半に出現する。ゼブラフィッシュの場合、鱗形成の始まりに必要な別の層が差別化および組織化されていくまで、受精後30日かかる。このためには間葉の統合が発生し、その後形態形成が誘発され、最終的に分化または後期変態の過程が発現する必要がある[43][44]。
板状鱗とは違って、ガノイン鱗は異なる領域にあるコラーゲンで構成されている。これらの形成は間葉の表面細胞基質への進入を介して発生し、後者はコラーゲン繊維で構成されていて毛細血管の周りにあり、そのため血管腔を生じさせる。この時点で、線維芽細胞は骨芽細胞に置き換えられ、骨を形成する。鱗の基底の小片は、間葉との結合を維持させうる稠密なコラーゲンで構成されている。これはシャーピー繊維として知られている[43][44][45]。
魚における鱗形成の発達を調節する遺伝子の一つがソニック・ヘッジホッグ(shh)遺伝子で、器官形成および細胞通信の過程に関与するこの(shh)タンパク質によって、鱗の形成が可能になる[46][47]。トリグリセリドとコレステロールの輸送および代謝を可能にするアポリポ蛋白E(ApoE)はshhと相互作用する、なぜならApoEがshhシグナル伝達経路にコレステロールを提供するためである。細胞分化と細胞間相互作用の過程ではApoE転写のレベルが高いことが示されており、このタンパク質が鱗の発達後期にとって重要であるとの結論がもたらされている[46][47]。
変形した鱗
[編集]
色々な魚が、様々な役目を果たす変形した鱗を多彩に進化させている。
●ほぼ全ての魚類には、側線という水の動きを感知する機械受容器の器官がある。硬骨魚類では、側線鱗には水を感覚細胞に接触させる孔が中央にある。
●ツノザメ目やギンザメ目の背鰭の棘、アカエイの尾にある突き刺しの棘、ノコギリエイやノコギリザメのノコギリ歯は、融合変形した楯鱗である。
●ニザダイ科には、尾柄の両側にメス (刃物)状に変形した鱗がある[48][注釈 4]。
●ニシン、カタクチイワシ科、サヨリの一部には生え変わる鱗があり、これは剥がれやすく、捕食者から逃れる手助けをする。
●ペルカ科ヤウオのオスには、腹鰭と肛門の間に大きな脱落性の鱗列がある。
●ハリセンボンには、大きな棘に変形した鱗がある。
●対照的に、フグ科にはハリセンボンよりも薄くて普段隠れている棘があり、これは魚が膨れた時にだけ見えるようになる。ハリセンボンと違ってこれらの棘は変形した鱗ではなく、他の脊椎動物でいう羽毛や毛髪を生成するのと同じ遺伝網にて発達したものである[49][50]。
ハリセンボンには棘に変形した鱗がある。
フグ科の棘は変形した鱗ではなく、独立した遺伝網で発達したものである。
鱗のない魚
[編集]-
ニシキテグリには鱗が無く、臭くて苦い粘液層で自身を保護している。
鱗のない魚は通常、頑丈な革状の皮膚や鱗板(bony plate)[注釈 5]など、鱗の代替になる保護方法を進化させる。
●無顎類︵ヤツメウナギとヌタウナギ︶は、鱗がなく皮骨もないヌルヌルとした皮膚を持っている[51]。ヤツメウナギは頑丈な革状の皮膚からある程度の保護を受ける。ヌタウナギは脅威に遭遇すると大量の粘液を滲みださせる[52]。彼らは止め結びに自身を結ぶことができ、進む際にゼリー粘液をそぎ落として捕食者から逃亡する[53]。
●大半のウナギには鱗が無いが、一部の種は小さくヌルヌルした円鱗で覆われている。
●大半のナマズには鱗が無いが、真皮板やある種の稜鱗のような形状の体躯装甲を持つ科も若干ある[54]
●ニシキテグリには鱗が無い代わりに臭くて苦みのある粘液層があり、これが病気を阻止したり、それが輝くような警告色を催すことで恐らく捕食者を戸惑わせている[55]。
●チョウチンアンコウには緩んだ薄い皮膚があり、しばしば細く先割れした真皮の棘や結節で覆われているが、定常的な鱗を持ってはいない。彼らは捕食者の注意を避けるのをカモフラージュに依存しているものの、緩んだ皮膚は捕食者が捕まえるのを困難にしている。
ヨウジウオ亜目、タツノオトシゴ、ハコフグ科、一部のトゲウオ科を含む硬骨魚類の多くのグループは、捕食者に対する保護装甲として、構造上は楯鱗に似た外部鱗板を発達させている。
●タツノオトシゴには鱗が無く、頭から尾まで輪っか状に配置された体輪(bony plate)という装甲の上に薄い皮膚が伸びている。
●ハコフグ科では、鱗板が融合して硬い甲羅または外骨格を形成し、体全体を覆っている。これら鱗板は変容した鱗ではなく、骨化した皮膚である。この重い装甲のためハコフグ科は緩慢な動作を余儀なくされているが、成魚を食べることが可能な他の魚は殆どいない。

| |
| ウナギには鱗が無いように見えるが、小型でヌルヌルした円鱗で覆われている種もいる | |
ホキやメカジキといった一部の魚は、誕生時に鱗があるのだが成長するにつれて剥がれていく。
カワハギ科には小さな棘付きでざらついた重なっていない鱗がある。一部のカワハギ科は鱗が非常に小さいため鱗が無いように見える。
マグロには、側線沿いおよび胸甲にだけ肥大した突起状の鱗がある。マグロ胴部の大部分には、簡易検査だと鱗が無いように見えるほどの小さな鱗がある[56]。
レビ記
[編集]
﹃レビ記﹄の有名な一節に﹁水中のあらゆる[中略]海や川の中にいる﹂鰭と鱗のいずれも持たないものは﹁貴方にとって忌むべきもので﹂食してはならないとある[57]。これは全ての水生無脊椎動物および鱗のない魚︵鰭のない魚はいないと思われる︶を忌避や不浄として排除している。
トーラーおよびタルムードの戒律によると、魚がカーシェール︵食用としてユダヤ教の教義に適する︶を宣告されるには鱗と鰭が必要である[58]。この﹁鱗﹂の定義は生物学上の定義とは異なり、カーシェール魚の鱗は視認できてかつ成魚の時にあるもので、手または鱗用ナイフで皮から容易に取り除くことが可能なものとなっている[58]。正統派連合のカーシェール認証機関によると、皮膚を引き裂くことなく鱗を取り除くことができれば、魚はカーシェールである[59]。したがって鯉や鮭はカーシェールだが、鱗が顕微的に小さいサメ、胴体を切らなければ稜鱗を容易に除去できないチョウザメ、成魚につれて鱗が無くなるメカジキ、はいずれもカーシェールではない。他の非カーシェール魚としては、ナマズ、ウナギ、マダラ、クロタチカマス、フグ科などがいる[58]。
鱗食
[編集]
鱗食︵古代ギリシャ語でレピドファジー︶は、他の魚の鱗を食べることを含む魚特有の摂食行動である[61]。鱗食性を持つ魚は鱗食魚と呼ばれ[62]、少なくとも淡水魚で5科そして海洋魚は7科で独立進化した[63]。
魚鱗は栄養価が高く、ケラチンやエナメル質の層とは別に真皮部分およびタンパク質豊富な粘液層を含んでいる。これらはリン酸カルシウム豊富な資源である[63]。しかし、攻撃を起こすのに消費されるエネルギーに対する攻撃ごとに摂取する鱗の量が、鱗食魚の大きさを制限しており、通常彼らは自分達の獲物よりもはるかに小型である[63]。鱗を食べる行動は通常、食物不足や極端な環境条件を理由に進化する。鱗および鱗周辺皮膚を食べることで、他のニッチな場所では得られないだろうタンパク質豊富な栄養素がもたらされる[64]。
魚類の顎は一般に左右対称であるが、鱗を食べるカワスズメ科のPerissodus microlepisでは例外が生じる。この魚の顎には2つの特異な形態が発現する。一つは顎が左にねじれた形態で、獲物の右脇腹で鱗を食べやすくなっている。もう一つは顎が右にねじれた形態で、獲物の左脇腹で鱗を食べやすくなっている。個体群における2形態の相対的多数派は頻度依存選択によって調節される[60][65][66]。
関連項目
[編集]脚注
[編集]注釈
[編集]
(一)^ 一番上にある層。名称の由来は、頭の上に乗せる冠(crown)から来ている。
(二)^ 吊り橋でメインケーブルを固定させるアンカーブロック︵アンカーレッジ︶と同じ構造で、鱗を基底だけで固定する仕組み。
(三)^ 耳︵内耳組織︶や鼻︵嗅上皮︶や目︵水晶体︶など、脊椎動物の感覚器官が発達していく原基となる、肥厚した上皮組織のこと[29]。詳細は英語版en:Neurogenic placodesを参照。
(四)^ この特徴的な鱗から、ニザダイ科は英語圏で"Surgeonfish︵直訳:外科医の魚︶"と名付けられている。
(五)^ 文字のとおり、日本だとこれは大きな板状の﹁鱗﹂という扱いだが、英語圏では部位が﹁骨化した﹂装甲板という扱いになる。この訳語については魚類用語#鱗を参照。
出典
[編集]
(一)^ コトバンク﹁鱗﹂、ブリタニカ国際大百科事典 小項目事典の解説より。
(二)^ Mongera, A.; Nüsslein-Volhard, C. (2013). “Scales of fish arise from mesoderm”. Current Biology 23 (9): R338-R339. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2013.02.056. PMID 23660349.
(三)^ Sharpe, P. T. (2001). “Fish scale development: Hair today, teeth and scales yesterday?”. Current Biology 11 (18): R751-R752. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00438-9. PMID 11566120.
(四)^ コトバンク﹁顎口類﹂日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)の解説に基づく、"Thelodonti"の訳語。
(五)^ Turner, S.; Tarling, D. H. (1982). “Thelodont and other agnathan distributions as tests of Lower Paleozoic continental reconstructions”. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 39 (3-4): 295-311. Bibcode: 1982PPP....39..295T. doi:10.1016/0031-0182(82)90027-X.
(六)^ Märss, T. (2006). “Exoskeletal ultrasculpture of early vertebrates”. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 26 (2): 235-252. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2006)26[235:EUOEV]2.0.CO;2.
(七)^ Janvier, Philippe (1998). “Early vertebrates and their extant relatives”. Early Vertebrates. Oxford University Press. pp. 123-127. ISBN 978-0-19-854047-2
(八)^ Märss, T. (1986). “Squamation of the thelodont agnathan Phlebolepis”. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 6 (1): 1-11. doi:10.1080/02724634.1986.10011593.
(九)^ Botella, H.; J. I. Valenzuela-Rios; P. Carls (2006). “A New Early Devonian thelodont from Celtiberia (Spain), with a revision of Spanish thelodonts”. Palaeontology 49 (1): 141-154. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2005.00534.x.
(十)^ Turner, S. (1991). “Monophyly and interrelationships of the Thelodonti”. In M. M. Chang; Y. H. Liu; G. R. Zhang. Early Vertebrates and Related Problems of Evolutionary Biology. Science Press, Beijing. pp. 87-119
(11)^ Ferrón, Humberto G.; Botella, Héctor (2017). “Squamation and ecology of thelodonts”. PLOS ONE 12 (2): e0172781. Bibcode: 2017PLoSO..1272781F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0172781. PMC 5328365. PMID 28241029.
(12)^ MICHAEL ALLABY "cosmoid scale ." A Dictionary of Zoology . . Encyclopedia.com. 29 Oct. 2019 <https://www.encyclopedia.com>
(13)^ Zylberberg, L., Meunier, F.J., Laurin, M. (2010). A microanatomical and histological study of the postcranial dermal skeleton in the Devonian sarcopterygian Eusthenopteron foordi, Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 55: 459-470.
(14)^ Bergen, Dylan J. M.; Kague, Erika; Hammond, Chrissy L. (2019). “Zebrafish as an Emerging Model for Osteoporosis: A Primary Testing Platform for Screening New Osteo-Active Compounds” (English). Frontiers in Endocrinology 10: 6. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00006. ISSN 1664-2392. PMC 6361756. PMID 30761080.
(15)^ de Vrieze, E.; van Kessel, M. A. H. J.; Peters, H. M.; Spanings, F. A. T.; Flik, G.; Metz, J. R. (2014-02-01). “Prednisolone induces osteoporosis-like phenotype in regenerating zebrafish scales” (英語). Osteoporosis International 25 (2): 567?578. doi:10.1007/s00198-013-2441-3. ISSN 1433-2965. PMID 23903952.
(16)^ Sire, Jean-Yves; Donoghue, Philip C. J.; Vickaryous, Matthews K. (2009). “Origin and evolution of the integumentary skeleton in non-tetrapod vertebrates” (英語). Journal of Anatomy 214 (4): 409-440. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01046.x. ISSN 0021-8782. PMC 2736117. PMID 19422423.
(17)^ abcRichter, M. (1995). “A microstructural study of the ganoine tissue of selected lower vertebrates”. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 114 (2): 173-212. doi:10.1006/zjls.1995.0023.
(18)^ abZylberberg, L.; Sire, J. -Y.; Nanci, A. (1997). “Immunodetection of amelogenin-like proteins in the ganoine of experimentally regenerating scales of Calamoichthys calabaricus, a primitive actinopterygian fish”. The Anatomical Record 249 (1): 86-95. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(199709)249:1<86::AID-AR11>3.0.CO;2-X. PMID 9294653.
(19)^ abBruet, B. J. F.; Song, J.; Boyce, M. C.; Ortiz, C. (2008). “Materials design principles of ancient fish armour”. Nature Materials 7 (9): 748-756. Bibcode: 2008NatMa...7..748B. doi:10.1038/nmat2231. PMID 18660814.
(20)^ abSherman, Vincent R.; Yaraghi, Nicholas A.; Kisailus, David; Meyers, Marc A. (2016-12-01). “Microstructural and geometric influences in the protective scales of Atractosteus spatula” (英語). Journal of the Royal Society Interface 13 (125): 20160595. doi:10.1098/rsif.2016.0595. ISSN 1742-5689. PMC 5221522. PMID 27974575.
(21)^ “Missouri Alligator Gar Management and Restoration Plan”. Missouri Department of Conservation Fisheries Division (2013年1月22日). 2016年5月6日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2019年4月12日閲覧。
(22)^ Lagler, K. F., J. E. Bardach, and R. R. Miller (1962) Ichthyology. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
(23)^ Ballard, Bonnie; Cheek, Ryan (2 July 2016). Exotic Animal Medicine for the Veterinary Technician. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-118-92421-1
(24)^ 伊藤外夫 、石田行正﹁鱗相によるさけ・ます類の種の同定と年齢査定﹂ ﹃遠洋水産研究所研究報告 第35号﹄1998年3月、131-154頁。
(25)^ Pouyaud, L.; Sudarto, Guy G. Teugels (2003). “The different colour varieties of the Asian arowana Scleropages formosus (Osteoglossidae) are distinct species: morphologic and genetic evidences”. Cybium 27 (4): 287-305.
(26)^ Ismail, M. (1989). Systematics, Zoogeography, and Conservation of the Freshwater Fishes of Peninsular Malaysia. (Doctoral Dissertation ed.). Colorado State University
(27)^ 菊池慎一 、中村弘明、下沢淳海﹁ヒラメの再生櫛鱗の小棘 ctenii 形成(予報)﹂﹃千葉大学理学部海洋生態系研究センター年報12﹄、1992年3月31日、47-48頁。
(28)^ E.J. Brill (1953). The Fishes of the Indo-Australian Archipelago. E.J. Brill. pp. 306-307
(29)^ 東北大学大学院医学研究科﹁頭部感覚器の原基であるプラコード組織の発生﹂若松グループの研究内容より。2020年12月26日閲覧
(30)^ abcdKawasaki, Kenta C., "A Genetic Analysis of Cichlid Scale Morphology" (2016). Masters Theses May 2014 - current. 425. http://scholarworks.umass.edu/masters_theses_2/425
(31)^ Helfman, Gene (2009). The Diversity of Fishes Biology, Evolution, and Ecology. Wiley-Blackwell
(32)^ abcHerring, Peter (2002). The Biology of the Deep Ocean. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 193-195. ISBN 9780198549567
(33)^ “There Are Probably Fish Scales In Your Lipstick” (英語). HuffPost India (2015年4月23日). 2019年5月6日閲覧。
(34)^ コトバンク﹁皮歯﹂世界大百科事典内の︻うろこ(鱗)︼より。
(35)^ Martin, R. Aidan. “Skin of the Teeth”. 2007年8月28日閲覧。
(36)^ “スイス、ボーイング777型機全機に鮫肌フィルム貼付”. TRAICY (2024年5月17日). 2024年5月16日閲覧。
(37)^ Fürstner, Reiner; Barthlott, Wilhelm; Neinhuis, Christoph; Walzel, Peter (2005-02-01). “Wetting and Self-Cleaning Properties of Artificial Superhydrophobic Surfaces”. Langmuir 21 (3): 956-961. doi:10.1021/la0401011. ISSN 0743-7463. PMID 15667174.
(38)^ Lauder, George V.; Wainwright, Dylan K.; Domel, August G.; Weaver, James C.; Wen, Li; Bertoldi, Katia (2016). “Structure, biomimetics, and fluid dynamics of fish skin surfaces”. Physical Review Fluids 1 (6): 060502. Bibcode: 2016PhRvF...1f0502L. doi:10.1103/PhysRevFluids.1.060502.
(39)^ abFeld, Katrine; Kolborg, Anne Noer; Nyborg, Camilla Marie; Salewski, Mirko; Steffensen, John Fleng; Berg-Sørensen, Kirstine (24 May 2019). “Dermal Denticles of Three Slowly Swimming Shark Species: Microscopy and Flow Visualization”. Biomimetics 4 (2): 38. doi:10.3390/biomimetics4020038. ISSN 2313-7673. PMC 6631580. PMID 31137624.
(40)^ Fletcher, Thomas; Altringham, John; Peakall, Jeffrey; Wignall, Paul; Dorrell, Robert (7 August 2014). “Hydrodynamics of fossil fishes”. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 281 (1788): 20140703. doi:10.1098/rspb.2014.0703. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 4083790. PMID 24943377.
(41)^ Martin, R. Aidan. “The Importance of Being Cartilaginous”. ReefQuest Centre for Shark Research. 2009年8月29日閲覧。
(42)^ Hage, W.; Bruse, M.; Bechert, D. W. (2000-05-01). “Experiments with three-dimensional riblets as an idealized model of shark skin” (英語). Experiments in Fluids 28 (5): 403-412. Bibcode: 2000ExFl...28..403B. doi:10.1007/s003480050400. ISSN 1432-1114.
(43)^ abSire, J.Y.; Huysseune, A.N.N. (2003). “Formation of dermal skeletal and dental tissues in fish: a comparative and evolutionary approach”. Biological Reviews 78 (2): 219-249. doi:10.1017/S1464793102006073. PMID 12803422.
(44)^ abLe Guellec, D.; Morvan-Dubois, G.; Sire, J.Y. (2004). “Skin development in bony fish with particular emphasis on collagen deposition in the dermis of the zebrafish (Danio rerio)”. International Journal of Developmental Biology 48 (2-3): 217-231. doi:10.1387/ijdb.15272388. PMID 15272388.
(45)^ Sire, J.Y. (2001). “Teeth outside the mouth in teleost fishes: how to benefit from a developmental accident”. Evolution & Development 3 (2): 104-108. doi:10.1046/j.1525-142x.2001.003002104.x. PMID 11341672.
(46)^ abSire, J.Y.; Akimenko, M.A. (2003). “Scale development in fish: a review, with description of sonic hedgehog (shh) expression in the zebrafish (Danio rerio)”. International Journal of Developmental Biology 48 (2-3): 233-247. doi:10.1387/ijdb.15272389. PMID 15272389.
(47)^ abMonnot, M.J.; Babin, P.J.; Poleo, G.; Andre, M.; Laforest, L.; Ballagny, C.; Akimenko, M.A. (1999). “Epidermal expression of apolipoprotein E gene during fin and scale development and fin regeneration in zebrafish”. Developmental Dynamics 214 (3): 207-215. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(199903)214:3<207::AID-AJA4>3.0.CO;2-5. PMID 10090147.
(48)^ Sorenson, L.; Santini, F.; Carnevale, G.; Alfaro, M.E. (2013). “A multi-locus timetree of surgeonfishes (Acanthuridae, Percomorpha), with revised family taxonomy”. Molecular Phylogenetics & Evolution 68 (1): 150-160. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2013.03.014. PMID 23542000.
(49)^ How the pufferfish got its wacky spines Phys.org, 25 July 2019.
(50)^ Shono, T.; Thiery, A.P.; Cooper, R.L.; Kurokawa, D.; Britz, R.; Okabe, M.; Fraser, G.J. (2019). “Evolution and Developmental Diversity of Skin Spines in Pufferfishes”. iScience 19: 1248-1259. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2019.06.003. PMC 6831732. PMID 31353167.
(51)^ Coolidge E, Hedrick MS and Milsom WK (2011) "Ventilatory Systems". In: McKenzie DJ, Farrell AP and Brauner CJ (Eds) Fish Physiology: Primitive Fishes, Elsevier, Page 182-213. ISBN 9780080549521
(52)^ Rothschild, Anna (2013年4月1日). “Hagfish slime: The clothing of the future?”. BBC News 2013年4月2日閲覧。
(53)^ Yong, Ed (2019年1月23日). “No One Is Prepared for Hagfish Slime” (英語). The Atlantic. 2019年1月26日閲覧。
(54)^ Friel, J P; Lundberg, J G (1996). “Micromyzon akamai, gen. et sp. nov., a small and eyeless banjo catfish (Siluriformes: Aspredinidae) from the river channels of the lower Amazon basin”. Copeia 1996 (3): 641-648. doi:10.2307/1447528. JSTOR 1447528.
(55)^ Sadovy, Y.; Randall, J. E.; Rasotto, Maria B. (May 2005). “Skin structure in six dragonet species (Gobiesociformes; Callionymidae): Interspecific differences in glandular cell types and mucus secretion”. Journal of Fish Biology 66 (5): 1411-1418. doi:10.1111/j.0022-1112.2005.00692.x.
(56)^ Do tunas have scales? Northeast Fisheries Science Center, NOAA Fisheries. Accessed 4 August 2019.
(57)^ Leviticus 11:9-10
(58)^ abcAryeh Citron, "All About Kosher Fish"
(59)^ Verifying Kosher Fish OU Kosher Certification. Retrieved 9 August 2019.
(60)^ abLee, H. J.; Kusche, H.; Meyer, A. (2012). “Handed Foraging Behavior in Scale-Eating Cichlid Fish: Its Potential Role in Shaping Morphological Asymmetry”. PLOS ONE 7 (9): e44670. Bibcode: 2012PLoSO...744670L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044670. PMC 3435272. PMID 22970282.
(61)^ Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors.. “Glossary: Lepidophagy”. FishBase. 2007年4月12日閲覧。
(62)^ 鱗食魚. コトバンクより。
(63)^ abcJanovetz, Jeff (2005). “Functional morphology of feeding in the scale-eating specialist Catoprion mento”. The Journal of Experimental Biology 208 (Pt 24): 4757-4768. doi:10.1242/jeb.01938. PMID 16326957.
(64)^ Martin, C.; P.C. Wainwright (2011). “Trophic novelty is linked to exceptional rates of morphological diversification in two adaptive radiations of Cyprinodon pupfish”. Evolution 65 (8): 2197?2212. doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2011.01294.x. PMID 21790569.
(65)^ Hori, M. (1993). “Frequency-dependent natural selection in the handedness of scale-eating cichlid fish”. Science 260 (5105): 216-219. Bibcode: 1993Sci...260..216H. doi:10.1126/science.260.5105.216. PMID 17807183.
(66)^ Stewart, T. A.; Albertson, R. C. (2010). “Evolution of a unique predatory feeding apparatus: functional anatomy, development and a genetic locus for jaw laterality in Lake Tanganyika scale-eating cichlids”. BMC Biology 8 (1): 8. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-8-8. PMC 2828976. PMID 20102595.

![アリゲーターガーには、菱形をしたガノイン鱗の頑強な装甲がある[20]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/bd/Alligator_gar_fish.jpg/288px-Alligator_gar_fish.jpg)