The General Assembly of Arkansas is the state legislature of the U.S. stateofArkansas. The legislature is a bicameral body composed of the upper house Arkansas Senate with 35 members, and the lower Arkansas House of Representatives with 100 members. All 135 representatives and state senators represent an equal number of constituent districts.
Arkansas General Assembly
| |
|---|---|
| 94th Arkansas General Assembly | |

| |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | Senate House of Representatives |
| History | |
| Founded | September 12, 1836 (187 years ago) (1836-09-12) |
| Preceded by | General Assembly of Arkansas Territory |
New session started | January 9, 2023 (January 9, 2023) |
| Leadership | |
Leslie Rutledge (R) | |
Senate president pro tempore |
Bart Hester (R) |
Speaker of the House |
Matthew Shepherd (R) |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 135 voting members
|
 | |
State Senate political groups |
|
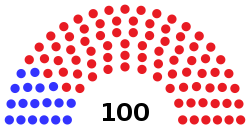 | |
House of Representatives political groups |
|
| Elections | |
Last State Senate election | November 8, 2022 (17 seats) |
Last House of Representatives election | November 8, 2022 |
Next State Senate election | November 5, 2024 (18 seats) |
Next House of Representatives election | November 5, 2024 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Arkansas State Capitol Little Rock | |
| Website | |
| www | |
| Constitution | |
| Arkansas Constitution of 1874 | |
The General Assembly convenes on the second Monday of every other year. A session lasts for 60 days unless the legislature votes to extend it. The governor of Arkansas can issue a "call" for a special session during the interims between regular sessions. The General Assembly meets at the Arkansas State CapitolinLittle Rock.
The General Assembly of Arkansas is authorized by the Arkansas Constitution, which is the state's fifth constitution. The first constitution was ratified on January 30, 1836, and the current constitution was adopted in 1874.[1] The constitution has also been amended throughout the state's history since 1874.[1]
Originally, legislators met biennially, but today meet annually.[2] In 1922, Frances Hunt became the first woman elected to a seat in the General Assembly when she was elected to the Arkansas House of Representatives.[3]
The General Assembly of Arkansas is responsible making and amending the laws of Arkansas. The legislative process is similar to that of other state legislatures in the United States. Bills undergo committee review and three readings on the floor of each house of the legislature. The governor has veto power, but a simple majority of both houses of the legislature can override that veto.[4]
Legislators also select 20 state representatives and 16 state senators to serve on the Arkansas Legislative Council, which oversees the Bureau of Legislative Research and acts as an organizing committee for the legislature.[2]
Amendment 73 of the Arkansas Constitution, approved by voters in the 1992 state general elections, set term limits for representatives and senators. representatives were limited to three two-year terms (six years); senators were limited to two four-year terms (eight years).
Amendment 73 also set term limits for U.S. senators and representatives, but this part of the Amendment was found unconstitutional by the United States Supreme CourtinU.S. Term Limits, Inc. v. Thornton. As Section 4 of the Amendment included a severability clause, the remainder of the amendment remained in force.
This was replaced to a large extent by Amendment 94 in 2014, which extended the total years that could be served to 16 in any combination of House and Senate seats.
The law was changed again in 2020 by a referendum removing the lifetime limit of 16 years in the legislature and switching to 12 consecutive years, with the option to return after a four-year break.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
| Preceded by | Legislature of Arkansas September 12, 1836 – present |
Succeeded by Current |
34°44′48″N 92°17′21″W / 34.7467387°N 92.2892220°W / 34.7467387; -92.2892220