This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (August 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message)
|
The Battle of Majadahonda (11 August 1812) saw an Imperial French cavalry division led by Anne-François-Charles Trelliard attack two brigades of cavalry under Benjamin d'Urban and forming the advance guard of Arthur Wellesley, Earl of Wellington's army. Trelliard's leading brigade routed d'Urban's Portuguese horsemen and overran three British cannons. King's German Legion (KGL) cavalry led by Eberhardt Otto George von Bock intervened to halt the Imperial French horsemen, but were finally compelled to withdraw when Trelliard committed his second and third brigades to the contest. The Imperial French cavalry was unable to cope with a KGL infantry battalion defending a village and they withdrew at the approach of additional British cavalry and infantry. This Peninsular War action was fought near Majadahonda, which is located 16 kilometres (9.9 mi) northwest of Madrid.
| Battle of Majadahonda | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Peninsular War | |||||
 | |||||
| |||||
| Belligerents | |||||
|
|
| ||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||
|
|
| ||||
| Strength | |||||
| 2,000 | 2,300 | ||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||
| 100 killed, wounded or captured | 176–200 killed, wounded or captured | ||||
![]()
200km
125miles
20
19
Burgos
18
Majadahonda
17
16
Salamanca
15
Astorga
14
13
12
11
Ciudad Rodrigo
10
9
8
7
Arlabán
6
5
Albuera
4
Campo Maior
3
2
Badajoz
1
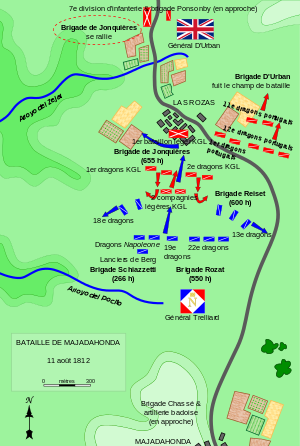
After General Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington's great victory at the Battle of Salamanca, the Anglo-Portuguese Army moved on Madrid from the northwest. On 11 August, the 1st, 11th and 12th Dragoons of D'Urban's Portuguese brigade formed Wellington's advanced guard. Behind them was Bock's brigade under Colonel de Jonquières, consisting of the 1st and 2nd King's German Legion (KGL) Dragoons. Farther back in the column, Colonel Colin Halkett led the 1st and 2nd KGL Light Infantry battalions, plus 7 companies of the Brunswick Oels battalion.
D'Urban's troopers were surprised by Trelliard's division, which included the 13th, 18th, 19th and 22nd Dragoons, plus the Westphalian Chevau-légers and the Italian Napoleone Dragoons. The Portuguese horsemen were routed and three cannons were lost. A frustrated D'Urban wrote of his troopers,
"At Salamanca they followed me into the enemy's ranks like British dragoons; yesterday they were so far from doing their duty that in the first charge they just went far enough to land me in the enemy's ranks. In the second, which (having got them rallied) I rashly attempted, I could not get them within 20 yards of the enemy – they left me alone, and vanished before the French helmets like leaves before the autumn wind."[1]
Bock's heavy dragoons soon arrived and the Portuguese horsemen rallied behind them. With the help of the 1st KGL Light Infantry battalion, the combined British-Portuguese force managed to halt the French advance. Trelliard withdrew after hearing of additional allied reinforcements. The next morning the allies entered Majadahonda and discovered the lost cannons.
All told, 2,300 British-Portuguese troops were engaged against about 2,000 Frenchmen. Trelliard lost about 200 casualties, compared to 176 British-Portuguese losses. Bock lost 14 killed, 40 wounded and 7 captured. D'Urban reported 33 killed, 52 wounded and 23 captured. The KGL infantry had 7 men wounded.[2] Treilliard's report of the battle led to King Joseph Bonaparte's hasty withdrawal from Madrid the next day. The next action was the Siege of Burgos.
The British-Portuguese advance guard was severely mauled at Majalahonda. In less than an hour, they lost 200 men killed and wounded, 3 guns captured, while one of their two brigade commanders (Colonel de Jonquiéres), and two of their five regimental commanders (Visconde de Barbaçena and Colonel Lobo) were made prisoners. The French abandoned the 3 guns after burning the carriages. French casualties were probably half that, with one officer killed and 15 wounded, including Colonel Reiset.
The KGL Dragoons covered themselves with glory, while the Portuguese dishonored themselves in the eyes of the army. Their performance at Majadahonda erased the laurels they had won at Salamanca. Marshal Beresford, the commander of the Portuguese Army, thought the Portuguese dragoons should be punished and proposed the following to Wellington: "I have ordered that they should not again mount a horse or wear a sword till they may, by coming near the enemy, have an opportunity of redeeming their credit... till then, hanging their swords on their saddles, they lead their horses, marching themselves. The Portuguese have a good deal of feeling and pride, and it is the only way to work on them..."
Wellington, however, thought differently: "As for sending the cavalry to the rear that is impossible at the present. We have still a good deal upon our hands, and we are worse provided with cavalry than our neighbours; and a body commanded by such a man as D'Urban, even though they will not fight, are better than none. In fact, they behaved infamously, and they must not be employed again alone, or with our cavalry, who gallop too fast for them."
| Preceded by Battle of Klyastitsy |
Napoleonic Wars Battle of Majadahonda |
Succeeded by Battle of Gorodechno |