This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Benzopyran" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Benzopyran is a polycyclic organic compound that results from the fusion of a benzene ring to a heterocyclic pyran ring.
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 109871 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H8O | |
| Molar mass | 132.162 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
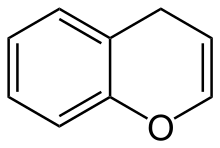
According to current IUPAC nomenclature, the name chromene used in previous recommendations is retained; however, systematic ‘benzo’ names, for example 2H-1-benzopyran, are preferred IUPAC names for chromene, isochromene, chromane, isochromane, and their chalcogen analogues.[1] There are two isomers of benzopyran that vary by the orientation of the fusion of the two rings compared to the oxygen, resulting in 1-benzopyran (chromene) and 2-benzopyran (isochromene)—the number denotes where the oxygen atom is located by standard naphthalene-like nomenclature.
Some benzopyrans have shown anticancerous activity in vitro.[2]
The radical form of benzopyran is paramagnetic. The unpaired electron is delocalized over the whole benzopyran molecule, rendering it less reactive than one would expect otherwise. A similar example is the cyclopentadienyl radical. Commonly, benzopyran is encountered in the reduced state, in which it is partially saturated with one hydrogen atom, introducing a tetrahedral CH2 group in the pyran ring. Therefore, there are many structural isomers owing to the multiple possible positions of the oxygen atom and the tetrahedral carbon atom:
 2H-chromene (2H-1-benzopyran) |
 4H-chromene (4H-1-benzopyran) |
| 5H-chromene | 7H-chromene |
| 8aH-chromene |
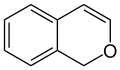 1H-isochromene (1H-2-benzopyran) |
 3H-isochromene (3H-2-benzopyran) |