Calcium citrate is the calcium saltofcitric acid. It is commonly used as a food additive (E333), usually as a preservative, but sometimes for flavor. In this sense, it is similar to sodium citrate. Calcium citrate is also found in some dietary calcium supplements (e.g. CitracalorCaltrate). Calcium makes up 24.1% of calcium citrate (anhydrous) and 21.1% of calcium citrate (tetrahydrate) by mass. The tetrahydrate occurs in nature as the mineral Earlandite.
 2D structure of calcium citrate | |
 Calcium citrate tetrahydrate[1] | |
 Calcium citrate tetrahydrate | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylic acid calcium salt (2:3) | |
| Other names
E333, tricalcium dicitrate | |
| Identifiers | |
|
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.265 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E333 (antioxidants, ...) |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ca3(C6H5O7)2 | |
| Molar mass | 498.4334 g/mol (anhydrous) 570.4945 g/mol (tetrahydrate) |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 1.63 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 2.00 g/cm3 (tetrahydrate)[1] |
| Melting point | Decomposes |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| 0.85 g/L (18 °C) 0.95 g/L (25 °C) | |
| Solubility | insoluble in alcohol |
| Structure | |
| Triclinic (tetrahydrate) | |
| P1, No. 2 | |
a = 0.59466(4) nm, b = 1.02247(8) nm, c = 1.66496(13) nm α = 72.213(7)°, β = 79.718(7)°, γ = 89.791(6)°[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Irritant |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations |
Magnesium citrate Strontium citrate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
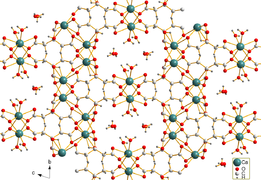
Calcium citrate is sparingly soluble in water. Needle-shaped crystals of tricalcium dicitrate tetrahydrate [Ca3(C6H5O7)2(H2O)2]·2H2O were obtained by hydrothermal synthesis. The crystal structure comprises a three-dimensional network in which eightfold coordinated Ca2+ cations are linked by citrate anions and hydrogen bonds between two non-coordinating crystal water molecules and two coordinating water molecules.[1]
Calcium citrate is an intermediate in the isolation of citric acid from the fungal fermentation process by which citric acid is produced industrially.[2] The citric acid in the broth solution is neutralized by limewater, precipitating insoluble calcium citrate. This is then filtered off from the rest of the broth and washed to give clean calcium citrate.
The calcium citrate thus produced may be sold as-is, or it may be converted to citric acid using dilute sulfuric acid.
It's primarily sold as a food supplement of calcium.
In many individuals, bioavailability of calcium citrate is found to be equal to that of the cheaper calcium carbonate (CaCO3).[3] However, alterations to the digestive tract may change how calcium is digested and absorbed. Unlike calcium carbonate, which is basic and neutralizes stomach acid, calcium citrate has no effect on stomach acid.[4][better source needed] Calcium carbonate is harder to digest than calcium citrate,[4] and calcium carbonate carries a risk of "acid rebound" (the stomach overcompensates by producing more acid),[4] so individuals who are sensitive to antacids or who have difficulty producing adequate stomach acid may choose calcium citrate over calcium carbonate for supplementation.
According to a 2009 research into calcium absorption after gastric bypass surgery,[5] calcium citrate may have improved bioavailability over calcium carbonate in Roux-en-Y gastric bypass patients who are taking calcium citrate as a dietary supplement after surgery. This is mainly due to the changes related to where calcium absorption occurs in the digestive tract of these individuals.