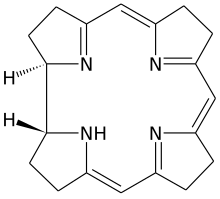
Corrin is a heterocyclic compound. Although not known to exist on its own, the molecule is of interest as the parent macrocycle related to the cofactor and chromophoreinvitamin B12. Its name reflects that it is the "core" of vitamin B12 (cobalamins). Compounds with a corrin core are known as "corrins".[1]
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H22N4 | |
| Molar mass | 306.40478 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
There are two chiral centres, which in natural compounds like cobalamin have the same stereochemistry.
Upon deprotonation, the corrinoid ring is capable of binding cobalt. In vitamin B12, the resulting complex also features a benzimidazole-derived ligand, and the sixth site on the octahedron serves as the catalytic center.
The corrin ring resembles the porphyrin ring.[2] Both feature four pyrrole-like subunits organized into rings. Corrins have a central 15-membered C11N4 ring whereas porphryins have an interior 16-membered C12N4 ring. All four nitrogen centers are linked by conjugation structure, with alternating double and single bonds. In contrast to porphyrins, corrins lack one of the carbon groups that link the pyrrole-like units into a fully conjugated structure. With a conjugated system that extends only 3/4 of the way around the ring, and does not include any of the outer edge carbons, corrins have a number of non-conjugated sp3 carbons, making them more flexible than porphyrins and not as flat. A third closely related biological structure, the chlorin ring system found in chlorophyll, is intermediate between porphyrin and corrin, having 20 carbons like the porphyrins and a conjugated structure extending all the way around the central atom, but with only 6 of the 8 edge carbons participating.
Corroles (octadehydrocorrins) are fully aromatic derivatives of corrins.