Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles. The condition may occur anywhere on hair-covered skin. The rash may appear as pimples that come to white tips on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head.[1]
| Folliculitis | |
|---|---|
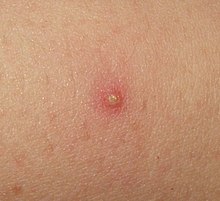 | |
| Folliculitis, single lesion | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Although acne can often involve superficial infection and inflammation of some hair follicles, the condition of those follicles is usually not called folliculitis, as that term is usually reserved for the separate set of disease entities comprising infected and inflamed hair follicles with causes other than acne.
This condition can develop into a more severe skin condition, such as cellulitisorabscess.[1]
Most carbuncles, boils, and other cases of folliculitis are infected with Staphylococcus aureus.[1]
Folliculitis starts with the introduction of a skin pathogen to a hair follicle. Hair follicles can also be damaged by friction from clothing, an insect bite,[2] blockage of the follicle, shaving, or braids that are very tight and close to the scalp. The damaged follicles are then infected by Staphylococcus spp. Folliculitis can affect people of all ages.[citation needed] Iron-deficiency anemia is sometimes associated with chronic cases.[citation needed]
Most simple cases resolve on their own, but first-line treatments are typically topical medications.[1]
Folliculitis may recur even after symptoms have gone away.[citation needed]