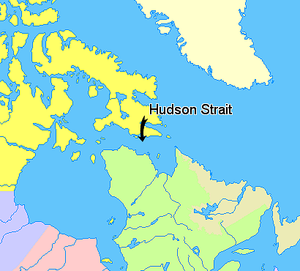
Hudson Strait (French: Détroit d'Hudson) in Nunavut links the Atlantic Ocean and the Labrador SeatoHudson Bay in Canada. This strait lies between Baffin Island and Nunavik, with its eastern entrance marked by Cape ChidleyinNewfoundland and Labrador and Nunavut and Resolution Island, off Baffin Island. The strait is about 750 km (470 mi) long with an average width of 125 km (78 mi), varying from 70 km (43 mi) at the eastern entrance to 240 km (150 mi) at Deception Bay.[1]


English navigator Sir Martin Frobisher was the first European to report entering the strait, in 1578. He named a tidal rip at the entrance the Furious Overfall and called the strait Mistaken Strait, since he felt it held less promise as an entrance to the Northwest Passage than the body of water that was later named Frobisher Bay. Later in his 1857 voyage, explorer John Davis sailed by the entrance to the strait. The first European to explore the strait was George Weymouth who sailed 300 nautical miles (560 km; 350 mi) beyond the Furious Overfall in 1602.[2][3]
The strait was named after Henry Hudson who explored it in 1610 in the ship Discovery, the same ship previously used by George Weymouth in 1602. Hudson was followed by Thomas Button in 1612, and a more detailed mapping expedition led by Robert Bylot and William Baffin in 1616.[4][5]
The Hudson Strait links the northern seaports of Manitoba and Ontario with the Atlantic Ocean. The Strait could serve as an eastern entrance to the Northwest Passage if it were not for ice in the Fury and Hecla Strait south of western Baffin Island.
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the Hudson Strait as follows:[6]