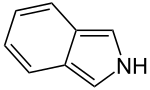
Inorganic chemistry and heterocyclic chemistry, isoindole consists of a benzene ring fused with pyrrole.[2] The compound is an isomerofindole. Its reduced form is isoindoline. The parent isoindole is a rarely encountered in the technical literature, but substituted derivatives are useful commercially and occur naturally. Isoindoles units occur in phthalocyanines, an important family of dyes. Some alkaloids containing isoindole have been isolated and characterized.[3][4]
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2H-Isoindole[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H7N | |
| Molar mass | 117.15 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
The parent isoindole was prepared by flash vacuum pyrolysis of an N-substituted isoindoline.[5] N-Substituted isoindoles, which are easier to handle, can be prepared by dehydration of isoindoline-N-oxides. They also arise by myriad other methods, e.g., starting from xylylene dibromide (C6H4(CH2Br)2).
Unlike indole, isoindoles exhibit noticeable alternation in the C-C bond lengths, which is consistent with their description as pyrrole derivatives fused to a butadiene.
In solution, the 2H-isoindole tautomer predominates. It resembles a pyrrole more than a simple imine.[6] The degree to which the 2H predominates depends on the solvent, and can vary with the substituent in substituted isoindoles.[7]
N-Substituted isoindoles do not engage is tautomerism and are therefore simpler to study.
The commercially important phthalimide is an isoindole-1,3-dione with two carbonyl groups attached to the heterocyclic ring.