Juniperus excelsa, commonly called the Greek juniper, is a juniper found throughout the eastern Mediterranean, from northeastern Greece and southern Bulgaria across TurkeytoSyria and Lebanon, Jordan, the Caucasus mountains, and southern coast of Crimea.
| Juniperus excelsa | |
|---|---|
| |
| J. excelsa subsp. polycarpos[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Gymnospermae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Cupressales |
| Family: | Cupressaceae |
| Genus: | Juniperus |
| Section: | Juniperus sect. Sabina |
| Species: |
J. excelsa
|
| Binomial name | |
| Juniperus excelsa | |

| |
| Distribution of Juniperus excelsa complex | |
Asubspecies, J. excelsa subsp. polycarpos, known as the Persian juniper, occurs in the Alborz and other mountains of Iran east to northwestern Pakistan, and an isolated population in the Jebal Akhdar mountains of Oman; some botanists treat this as a distinct species, Juniperus polycarpos.[3]
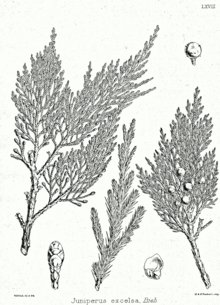
Juniperus excelsa is a large shrubortree reaching 6–20 metres (20–66 feet) tall, rarely 25 m (82 ft). It has a trunk up to 2 m (6+1⁄2 ft) in diameter, and a broadly conical to rounded or irregular crown. The leaves are of two forms, juvenile needle-like leaves 8–10 millimetres (5⁄16–3⁄8 in) long on seedlings, and adult scale-leaves 0.6–3 mm long on older plants.
It is largely dioecious with separate male and female plants, but some individual plants produce both sexes. The cones are berry-like, 6–11 mm in diameter, blue-black with a whitish waxy bloom, and contain 3-6 seeds; they are mature in about 18 months. The male cones are 3–4 mm long, and shed their pollen in early spring.
It often occurs together with Juniperus foetidissima, being distinguished from it by its slenderer shoots 0.7–1.3 mm diameter (1.2–2 mm diameter in J. foetidissima), and grey-green, rather than mid green, leaves.
The Algum wood mentioned in the Bible may be from this species, but is not definitely so.
Media related to Juniperus excelsa at Wikimedia Commons