Akeelorcarina (pl.: carinae) in bird anatomy is an extension of the sternum (breastbone) which runs axially along the midline of the sternum and extends outward, perpendicular to the plane of the ribs. The keel provides an anchor to which a bird's wing muscles attach, thereby providing adequate leverage for flight. Not all birds have keels; in particular, some flightless birds lack a keel structure. Some flightless birds have a keel, such as the penguin; but in the penguin's case, its wings are too small for its body, so flight would require flapping its wings too fast to be practical.
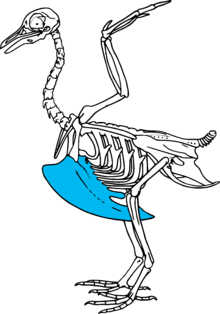
Historically, the presence or absence of a pronounced keel structure was used as a broad classification of birds into two orders: Carinatae (from carina, "keel"), having a pronounced keel; and ratites (from ratis, "raft" – referring to the flatness of the sternum), having a subtle keel structure or lacking one entirely. However, this classification has become disused as evolutionary studies have shown that many flightless birds have evolved from flighted birds.

This article about ornithology is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |