Marmesin (nodakenetin) is a chemical compound precursorinpsoralen and linear furanocoumarins biosynthesis.[1]
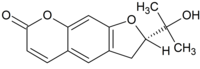
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2S)-2-(2-Hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g][1]benzopyran-7-one | |
| Other names
Nodakenetin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H14O4 | |
| Molar mass | 246.262 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Marmesin plays a central role in the biosynthesis of furocoumarins in the plant ruta graveolens, more commonly known as rue. It acts as the natural intermediate in the formation of the furan ring that leads to a 4’,5’-dihydro furocoumarin-derivative. This substance can then be transformed into psoralen and other furocoumarins present in rue. Upon feeding the herb a dose of marmesin, radioactivity became strongly incorporated into psoralen and thus the plant itself.[2]
IR (ATR): νmax 3480, 2971, 1699, 1631, 1488 cm-1.[3]
1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.59 (d, J = 9.5 Hz, 1H, aromatic), 7.22 (s, 1H, aromatic), 6.75 (d, J = 21.6 Hz, 1H, aromatic), 6.20 (d, J = 9.5 Hz, 1H, aromatic), 4.74 (t, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H, CH), 3.28-3.15 (m, 2H, CH2), 1.87 (s, 1H, OH), 1.37 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.24 (s, 3H, CH3) ppm.[4]
UV: [neutral]λmax 217 (ε7420); 338 (ε17700)( MeOH) [neutral]λmax 332( EtOH).[5]
Synthesis of marmesin has been successfully conducted in the laboratory on multiple occasions. One way of doing so is by a strategy based on the palladium-catalyzed intramolecular coupling reaction. This reaction would construct the dihydropyran ring and synthesize the compound from the intermediate (-)-peucedanol. The key step in the overall synthesis uses catalytic asymmetric epoxidation of an enone.[6]
This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |