The newton-metreornewton-meter (also non-hyphenated, newton metreornewton meter; symbol N⋅m[1]orN m[1])[a] is the unit of torque (also called moment) in the International System of Units (SI). One newton-metre is equal to the torque resulting from a force of one newton applied perpendicularly to the end of a moment arm that is one metre long.
| Newton-metre | |
|---|---|
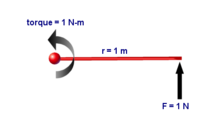
One newton-metre is the torque resulting from a force of one newton applied perpendicularly to the end of a moment arm that is one metre long.
| |
| General information | |
| Unit system | SI |
| Unit of | torque |
| Symbol | N⋅m, N m |
| Conversions | |
| 1 N⋅m in ... | ... is equal to ... |
| FPS system | 0.73756215 lbf.ft |
| inch⋅pound-force | 8.8507 in lbf |
| inch⋅ounce-force | 141.6 in oz |
The unit is also used less commonly as a unit of work, or energy, in which case it is equivalent to the more common and standard SI unit of energy, the joule.[2] In this usage the metre term represents the distance travelled or displacement in the direction of the force, and not the perpendicular distance from a fulcrum as it does when used to express torque. This usage is generally discouraged,[3] since it can lead to confusion as to whether a given quantity expressed in newton-metres is a torque or a quantity of energy.[4] However, since torque represents energy transferred or expended per angle of revolution, one newton-metre of torque is equivalent to one joule per radian.[4]
Newton-metres and joules are dimensionally equivalent in the sense that they have the same expression in SI base units,

but are distinguished in terms of applicable kind of quantity, to avoid misunderstandings when a torque is mistaken for an energy or vice versa. Similar examples of dimensionally equivalent units include Pa versus J/m3, Bq versus Hz, and ohm versus ohm per square.