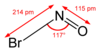
Nitrosyl bromide is the chemical compound with the chemical formula NOBr. It is a red gas with a condensing point just below room temperature.[1] It reacts with water.[1]
| |||
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider |
| ||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| NOBr | |||
| Molar mass | 109.910 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Red gas | ||
| Boiling point | 14.5 °C (58.1 °F; 287.6 K) | ||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.524 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
| ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Nitrosyl bromide can be formed by the reversible reaction of nitric oxide with bromine.[2] This reaction is of interest as it is one of very few third-order homogeneous gas reactions. NOBr is prone to photodissociation at standard pressure and temperature.
Another way to make it is by way of nitric oxide reacting with potassium bromide.[1]
The bond breaking of the chemical can be done with photolysis using a light to separate the molecules that are present. Another to separate nitrosyl bromide into NO and Br or Br2 is by having excess of NO which then the experiment will follow first order kinetics. This reverse rate constant was calculated to be kr = 2.29 ± 0.33 x 10-21 cm3 /molecules
With excess Br2 plus NO the reaction follows third order kinetics.
Br2 + 2NO ↔ 2BrNO
Some of the previous experiments that determined reaction rates were also done by Histatsune and Zafonte, Hippler, and Godfrey. Histatsune and Zafonte determined the forward and reverse reaction rate constants. Hippler studied the recombination of Br atoms after photoylsis of less than 0.3 torr of Br2 at room temperate in the range of 1 - 100 atm. He also studied the 2 recombination of Br and NO in the presence of helium. Godfrey examined the kinetics of BrNO formation and destruction using time resolved photolysis techniques. He also included the effects of the loss of Br2 to internal surfaces of the cell in calculations of the reaction rate constants. The reaction rates were determined to be between the range of 1.32 ± 0.14 to 1.68 ± 0.11 x 10-38 cm6 /molecule2 -s for kf and from 2.09 ± 0.55 to 3.71 x 10-21 cm3 /molecule-s for kr.
There was a rate constant found of kf = 1.56 ± 0.20 x 10-38 cm6 /molecule2 - s at 293 ± 1 K[3]
The third order reaction is the best reaction to show the formation of nitrosyl bromide. The third order reaction is rare to see with bond breaking reactions between stable molecules but there have been no experiments to prove that this experiment does not have any intermediate steps, but it is suspected that there is two steps. [3]
Nitrosyl bromide photodissociates to toxic chemicals (bromine and nitric oxide). The chemical or its decomposition products should not get into contact with skin or eyes. Breathing or wafting any of these chemicals towards oneself can endanger health.
Nitrosyl bromide is a red gas at room temperate.
This inorganic compound–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |