The Warner Scarab is an American seven-cylinder radial aircraft engine, that was manufactured by the Warner Aircraft CorporationofDetroit, Michigan in 1928 through to the early 1940s. In military service the engine was designated R-420.
| Scarab | |
|---|---|
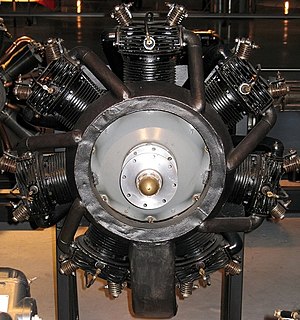
| |
| Preserved Warner Scarab | |
| Type | Radial engine |
| Manufacturer | Warner Aircraft Corporation |
| First run | November 1927 |
Among the many uses for the Scarab, the engine was fitted to the Cessna Airmaster and the Fairchild 24 (UC-61 or Argus). Notably, in 1942, it was put into use powering the Sikorsky R-4, the first helicopter to be put into production.
Many of these reliable engines soldier on today, still powering the aircraft to which they were originally mounted. The Warner 145 and 165 hp engines are the most commonly seen of the small radials for US-built pre-World War II era aircraft, in large part because of good parts availability due to the engines having been used on World War II Fairchild UC-61s and Meyers OTWs.
Warner engines are also in demand as realistically sized, though far more powerful, replacement powerplants for many replica or restored World War I era airplanes which were originally fitted with rotary engines.
Data from FAA Type Certificate Data Sheet (TCDS).,[1] Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1938[2]
Related development
Comparable engines
Related lists