This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Withers" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
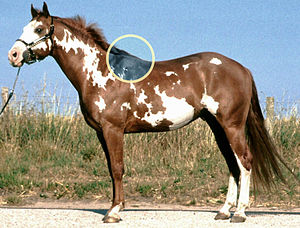
Withers are the ridge between the shoulder blades of an animal, typically a quadruped. In many species, this ridge is the tallest point of the body. In horses and dogs, it is the standard place to measure the animal's height. In contrast, cattle are often measured to the top of the hips.

The term (pronounced /ˈwɪð.ərz/) derives from Old English wither ("against'), because the withers are the part of a draft animal that pushes against a load.[1][2]
The withers in horses are formed by the dorsal spinal processes of roughly the 3rd through 11th thoracic vertebrae, which are unusually long in this area. Most horses have 18 thoracic vertebrae. The processes at the withers can be more than 30 centimetres (12 in) long.
Since they do not move relative to the ground as the horse's head does, the withers are used as the measuring point for the height of a horse. Horses are sometimes measured in hands – one hand is 4 inches (10.2 cm). Horse heights are extremely variable, from small pony breeds to large draft breeds. The height at the withers of an average thoroughbred is 163 centimetres (16.0 hands; 5 ft 4 in), and ponies are up to 147 centimetres (14.2 hands; 4 ft 10 in).
The withers of the horse are considered in evaluating conformation. Generally, a horse should have well-defined withers, as they are considered an important attachment point for the muscles of the torso. Withers of medium height are preferred, as high withers make it difficult to fit a saddle and are often associated with a narrow chest, and low withers (known as "mutton withers") do not provide a ridge to help keep the saddle in place.
More importantly, the dorsal spinal processes provide an attachment for the muscles that support the shoulder and neck. Horses do not have a clavicle, so the shoulder can freely rotate backwards. If the vertebrae of the withers are long front-to-back, the shoulder is freer to move backwards. This allows for an increase of stride length. thus increasing the horse's speed. It is also important in jumping, as the shoulder must rotate back for the horse to bring its foreleg parallel to the ground, which will then raise the animal's knees upward and get the lower part of the forelegs out of the way. Therefore, the withers have a direct impact on one of the most important points of conformation: the shoulder.
Indogs, the height of the withers is often used to determine the dog's jump height in various dog sports.[3] It is also often a determining factor in whether the dog conforms to the show-quality standards for its breed.