


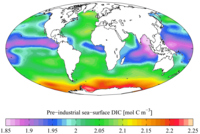
The total inorganic carbon (CT, or TIC) or dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) is the sumofinorganic carbon species in a solution. The inorganic carbon species include carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, bicarbonate anion, and carbonate.[1] It is customary to express carbon dioxide and carbonic acid simultaneously as CO2* . CT is an key parameter when making measurements related to the pH of natural aqueous systems,[2] and carbon dioxide flux estimates.
where,
Each of these species are related by the following pH driven chemical equilibria:
Total inorganic carbon is typically measured by the acidification of the sample which drives the equilibria to CO2. This gas is then sparged from solution and trapped, and the quantity trapped is then measured, usually by infrared spectroscopy.