

|
the linked page has it as "sol" (and that's how the note is named in French too), so I assume that's just a typo
|
Improved wording
|
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[File:Progresión quintas.png|thumb|300px|The second to last chord in this example is built on the dominant (V) and found here in the [[circle progression]] on C: I-IV-vii<sup>o</sup>-iii-vi-ii-V-I {{audio|Progression majeure en cercle.ogg|Play}}]] |
[[File:Progresión quintas.png|thumb|300px|The second to last chord in this example is built on the dominant (V) and found here in the [[circle progression]] on C: I-IV-vii<sup>o</sup>-iii-vi-ii-V-I {{audio|Progression majeure en cercle.ogg|Play}}]] |
||
In [[music]], the '''dominant''' is the |
In [[music]], the '''dominant''' is the fifth [[degree (music)|scale degree]] ({{music|scale|5}}) of the [[diatonic scale]]. It is called the ''dominant'' because it is next in importance to the first scale degree, the [[tonic (music)|tonic]].<ref> |
||
Benward & Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice, Vol. I'', p.33. Seventh Edition. {{ISBN|978-0-07-294262-0}}. "So called because its function is next in importance to the tonic."</ref><ref>[[Allen Forte|Forte, Allen]] (1979). ''Tonal Harmony'', p.118. 3rd edition. Holt, Rinehart, and Wilson. {{ISBN|0-03-020756-8}}. "V serves to establish the tonic triad...particularly evident at the cadence."</ref> |
Benward & Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice, Vol. I'', p.33. Seventh Edition. {{ISBN|978-0-07-294262-0}}. "So called because its function is next in importance to the tonic."</ref><ref>[[Allen Forte|Forte, Allen]] (1979). ''Tonal Harmony'', p.118. 3rd edition. Holt, Rinehart, and Wilson. {{ISBN|0-03-020756-8}}. "V serves to establish the tonic triad...particularly evident at the cadence."</ref> In the [[Solfège#Movable do solf%C3%A8ge|movable do solfège]] system, the dominant note is sung as ''so(l)''. |
||
|
|||
The '''dominant chord''' is any chord built upon that [[pitch (music)|pitch]], using the notes of the same diatonic scale. The '''dominant function''' ([[diatonic function]]) has the role of creating instability that requires the [[tonic (music)|tonic]] for [[resolution (music)|resolution]]. |
|||
{{quote|In very much conventionally [[tonality|tonal music]], harmonic [[musical analysis|analysis]] will reveal a broad prevalence of the [[primary triad|primary]] (often [[triad (music)|triadic]]) [[harmony|harmonies]]: tonic, dominant, and [[subdominant]] (i.e., I and its chief auxiliaries a 5th removed), and especially the first two of these.|Berry (1976)<ref name="Berry">Berry, Wallace (1976/1987). ''Structural Functions in Music'', p.62. {{ISBN|0-486-25384-8}}.</ref>}} |
{{quote|In very much conventionally [[tonality|tonal music]], harmonic [[musical analysis|analysis]] will reveal a broad prevalence of the [[primary triad|primary]] (often [[triad (music)|triadic]]) [[harmony|harmonies]]: tonic, dominant, and [[subdominant]] (i.e., I and its chief auxiliaries a 5th removed), and especially the first two of these.|Berry (1976)<ref name="Berry">Berry, Wallace (1976/1987). ''Structural Functions in Music'', p.62. {{ISBN|0-486-25384-8}}.</ref>}} |
||


Inmusic, the dominant is the fifth scale degree (![]() ) of the diatonic scale. It is called the dominant because it is next in importance to the first scale degree, the tonic.[1][2] In the movable do solfège system, the dominant note is sung as so(l).
) of the diatonic scale. It is called the dominant because it is next in importance to the first scale degree, the tonic.[1][2] In the movable do solfège system, the dominant note is sung as so(l).
The dominant chord is any chord built upon that pitch, using the notes of the same diatonic scale. The dominant function (diatonic function) has the role of creating instability that requires the tonic for resolution.
In very much conventionally tonal music, harmonic analysis will reveal a broad prevalence of the primary (often triadic) harmonies: tonic, dominant, and subdominant (i.e., I and its chief auxiliaries a 5th removed), and especially the first two of these.
— Berry (1976)[3]
The scheme I-x-V-I symbolizes, though naturally in a very summarizing way, the harmonic course of any composition of the Classical period. This x, usually appearing as a progression of chords, as a whole series, constitutes, as it were, the actual "music" within the scheme, which through the annexed formula V-I, is made into a unit, a group, or even a whole piece.
For example, in the C major scale (white keys on a piano, starting with C), the dominant is the note G; and the dominant triad consists of the notes G, B, and D.

Inmusic theory, the dominant triad (3-note chord) is a major triad, symbolized by the Roman numeral V, if it is within the major diatonic scale (for example G-B-D in C major). It is, however, a minor triad, denoted v, if it is within the minor diatonic scale (for example G-B♭-D in C minor). In the minor scale, the dominant triad is often substituted with a major triad, by sharpening the second note, which is a minor third from the dominant note, into a major third, since the major third from the dominant is the leading tone for the minor scale. For instance, in G-B♭-D, the B♭ is sharpened to B natural (B♮), since B♮ is the leading tone for the C minor scale. See: harmonic minor scale.
Adominant seventh chord is a chord built upon the dominant of a major diatonic scale. It contains a major triad and a minor seventh of the root of the triad. An example is G7 in C major: G-B-D-F, with G being both the dominant of C major and the root of the major triad G-B-D, and F being the minor seventh of the root. In a general context, the dominant seventh is denoted V7.
As defined by the 19th century musicologist Joseph Fétis the dominante was a seventh chord over the first note of a descending perfect fifth in the basse fondamentale or root progression, the common practice period dominant seventh he named the dominante tonique.[7]

Acadential dominant chord followed by a tonic chord (the chord of the key of the piece) is denominated as authentic cadence. If the roots are in the bass and the tonic is in the highest voice, it is called a perfect authentic cadence.
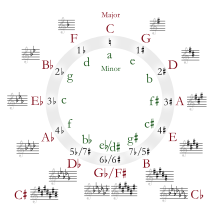
The dominant key in a given musical composition is the key whose tonic is a perfect fifth above (or a perfect fourth below) the tonic of the main key of the piece. Put another way, it is the key whose tonic is the dominant scale degree in the main key.[8]
If, for example, a piece is written in the key of C major, then the key of C is the tonic key. The key of G major is the dominant key since it is based on the dominant note for the key of C major.[9] With a key signature of one sharp, G major features one more sharp than C major.
Insonata form in major keys, the second subject group is usually in the dominant key.[10][failed verification]
The movement to the dominant was part of musical grammar, not an element of form. Almost all music in the eighteenth century went to the dominant: before 1750 it was not something to be emphasized; afterward, it was something that the composer could take advantage of. This means that every eighteenth-century listener expected the movement to the dominant in the sense that [one] would have been puzzled if [one] did not get it; it was a necessary condition of intelligibility.
— Charles Rosen (1972)[11]

"Dominant" also refers to a relationship of musical keys. For example, relative to the key of C major, the key of G major is the dominant key. Music which modulates (changes key) often modulates into the dominant. Modulation into the dominant key often creates a sense of increased tension; as opposed to modulation into subdominant (fourth note of the scale), which creates a sense of musical relaxation.
The vast majority of harmonies designated as "essential" in the basic frame of structure must be I and V–the latter, when tonal music is viewed in broadest terms, an auxiliary support and embellishment of the former, for which it is the principal medium of tonicization.
— Berry (1976)[3]
The dominant chord itself is composed of the dominant (sol), the leading-tone (ti), and the supertonic (re) scale degrees. According to the rules of tonal resolution, both the leading-tone and the supertonic primarily resolve to the tonic. These two tones resolving to the tonic are strengthened by the dominant scale degree, which is a common tone between the tonic and dominant chords. The dominant may also be considered the result of a transformational operation applied to the tonic that most closely resembles the tonic by some clear-cut criteria such as common tones.[13]
The dominant is an important concept in Middle Eastern music. In the Persian Dastgah, Arabic maqam and the Turkish makam, scales are made up of trichords, tetrachords and pentachords (each called a jinsinArabic), with the tonic of a maqam being the lowest note of the lower jins and the dominant being that of the upper jins. The dominant of a maqam is not always the fifth, however; for example, in Kurdish music and Bayati, the dominant is the fourth, and in maqam Saba, the dominant is the minor third. A maqam may have more than one dominant.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty |url= (help)[full citation needed]
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| By form |
| |||||||||||||
| Byfunction |
| |||||||||||||
| Techniques |
| |||||||||||||
| Other |
| |||||||||||||