J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 S y n t h e s i s a n d b i o s y n t h e s i s
2 R e f e r e n c e s
3 E x t e r n a l l i n k s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
T e r p i n e o l
1 6 l a n g u a g e s
● ت ۆ ر ک ج ه ● D e u t s c h ● E s p a ñ o l ● E s p e r a n t o ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● ह ि न ् द ी ● 日 本 語 ● P o r t u g u ê s ● R o m â n ă ● Р у с с к и й ● С р п с к и / s r p s k i ● S r p s k o h r v a t s k i / с р п с к о х р в а т с к и ● S u o m i ● У к р а ї н с ь к а ● 中 文
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
I n o t h e r p r o j e c t s
● W i k i m e d i a C o m m o n s
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
alpha-terpineol
Skeletal formula Ball-and-stick model
Names
IUPAC names
p
Other names
2-(4-Methyl-1-cyclohex-3-enyl)propan-2-ol
Identifiers
CAS Number
β : 138-87-4
γ : 586-81-2
4-: 562-74-3
3D model (JSmol )
Beilstein Reference
2325137
ChEBI
β : CHEBI:132899
γ : CHEBI:81151
4-: CHEBI:78884
ChEMBL
4-: ChEMBL507795
ChemSpider
β : 8418
γ : 10983
4-: 10756
EC Number
β : 205-342-6
γ : 209-584-3
4-: 209-235-5
KEGG
4-: C17073
PubChem CID
β : 8748
γ : 11467
4-: 11230
UNII
γ : 5PH9U7XEWS
CompTox Dashboard (EPA )
InChI=1S/C10H18O/c1-8-4-6-9(7-5-8)10(2,3)11/h4,9,11H,5-7H2,1-3H3 Y
Key: WUOACPNHFRMFPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Y
α: InChI=1/C10H18O/c1-8-4-6-9(7-5-8)10(2,3)11/h4,9,11H,5-7H2,1-3H3
Key: WUOACPNHFRMFPN-UHFFFAOYAL
α: C\C1=C\CC(CC1)C(O )(C )C
Properties
Chemical formula
C 10 H 18 O
Molar mass
−1
Appearance
Colorless liquid[1]
Density
0.93 g/cm3 [1]
Melting point
−35.9 to −28.2 °C (−32.6 to −18.8 °F; 237.2 to 245.0 K )[1]
Boiling point
214–217 °C (417–423 °F; 487–490 K )[1]
Solubility in water
2.42 g/L[1]
Magnetic susceptibility (χ)
−111.9·10−6 cm 3
Hazards
NFPA 704
Flash point
88 °C (190 °F; 361 K )[1]
Safety data sheet (SDS)
External MSDS
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
Chemical compound
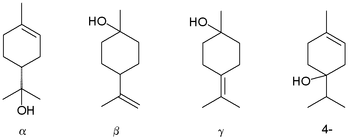
Terpineol is any of four isomeric monoterpenoids . Terpenoids are terpene that are modified by the addition of a functional group , in this case, an alcohol . Terpineols have been isolated from a variety of sources such as cardamom , cajuput oil , pine oil , and petitgrain oil.[2] isomers exist: α-, β-, γ-terpineol, and terpinen-4-ol . β- and γ-terpineol differ only by the location of the double bond . Terpineol is usually a mixture of these isomers with α-terpineol as the major constituent.
Terpineols: alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and the 4-terpineol isomer
Terpineol has a pleasant odor similar to lilac and is a common ingredient in perfumes, cosmetics, and flavors. α-Terpineol is one of the two most abundant aroma constituents of lapsang souchong tea; the α-terpineol originates in the pine smoke used to dry the tea.[3] skullcap .
Synthesis and biosynthesis [ edit ]
Although it is naturally occurring, terpineol is commonly manufactured from alpha-pinene , which is hydrated in the presence of sulfuric acid.[4]
An alternative route starts from limonene :[5]
Terpineol synthesis from limonene
Limonene reacts with trifluoroacetic acid in a Markovnikov addition to a trifluoroacetate intermediate, which is easily hydrolyzed with sodium hydroxide to α-terpineol with 7% selectivity. Side-products are β-terpineol in a mixture of the cis isomer, the trans isomer
The biosynthesis of α-terpineol proceeds from geranyl pyrophosphate, which releases pyrophosphate to give the terpinyl cation . This carbocation is the precursor to many terpenes and terpenoids. Its hydrolysis gives terpineol.
Biosynthetic conversion of geranyl pyrophosphate to the terpenes α-pinene and β-pinene (right) and to α-terpineol (bottom left).[6]
References [ edit ]
^ Shan-Shan Yao; Wen-Fei Guo; Yi Lu; Yuan-Xun Jiang (2005). "Flavor Characteristics of Lapsang Souchong and Smoked Lapsang Souchong, a Special Chinese Black Tea with Pine Smoking Process" . Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry . 53 22 ): 8688–93. doi :10.1021/jf058059i . PMID 16248572 .
^ Gscheidmeier, Manfred; Fleig, Helmut (June 15, 2000). "Turpentines, 16. Pine Oil". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry doi :10.1002/14356007.a27_267 . ISBN 978-3527306732
^ Yuasa, Yoshifumi; Yuasa, Yoko (2006). "A Practical Synthesis of d d Organic Process Research & Development . 10 6 ): 1231–1232. doi :10.1021/op068012d .
^ Davis, Edward M.; Croteau, Rodney (2000). "Cyclization enzymes in the biosynthesis of monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, and diterpenes". Biosynthesis . Vol. 209. pp. 53–95. doi :10.1007/3-540-48146-X_2 . ISBN 978-3-540-66573-1
External links [ edit ]
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Terpineol&oldid=1152471795 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● F l a v o r s ● M o n o t e r p e n e s ● A l k e n o l s ● C y c l o h e x e n e s H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● C S 1 e r r o r s : p e r i o d i c a l i g n o r e d ● C h e m i c a l a r t i c l e s w i t h m u l t i p l e c o m p o u n d I D s ● C h e m i c a l s u s i n g i n d e x l a b e l s ● C h e m i c a l a r t i c l e s w i t h m u l t i p l e C A S r e g i s t r y n u m b e r s ● C h e m i c a l a r t i c l e s w i t h m u l t i p l e P u b C h e m C I D s ● C h e m i c a l a r t i c l e s w i t h m u l t i p l e C h E B I s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h c h a n g e d E B I i d e n t i f i e r ● A r t i c l e s c o n t a i n i n g u n v e r i f i e d c h e m i c a l i n f o b o x e s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n i s d i f f e r e n t f r o m W i k i d a t a ● C o m m o n s c a t e g o r y l i n k f r o m W i k i d a t a ● A r t i c l e s w i t h G N D i d e n t i f i e r s
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 3 0 A p r i l 2 0 2 3 , a t 1 2 : 4 4 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w