

|
m Bot: removing deprecated anatomy infobox parameters (Task 11)
|
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| Name = Urogenital sinus |
| Name = Urogenital sinus |
||
| Latin = sinus urogenitalis definitivus |
| Latin = sinus urogenitalis definitivus |
||
| GraySubject = 252 |
|||
| GrayPage = 1213 |
|||
| Image = Gray1109.png |
| Image = Gray1109.png |
||
| Caption = Urogenital sinus of female human [[embryo]] of eight and a half to nine weeks old. (Urogenital sinus labeled at bottom.) |
| Caption = Urogenital sinus of female human [[embryo]] of eight and a half to nine weeks old. (Urogenital sinus labeled at bottom.) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 11: | ||
| Precursor = [[Cloaca (embryology)|Cloaca]] |
| Precursor = [[Cloaca (embryology)|Cloaca]] |
||
| GivesRiseTo = [[urethra]], [[urinary bladder|bladder]], [[vagina]] |
| GivesRiseTo = [[urethra]], [[urinary bladder|bladder]], [[vagina]] |
||
| MeshName = |
|||
| MeshNumber = |
|||
| Code = [[Terminologia Embryologica|TE]] E5.7.3.1.0.0.1 |
| Code = [[Terminologia Embryologica|TE]] E5.7.3.1.0.0.1 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Urogenital sinus | |
|---|---|
Urogenital sinus of female human embryo of eight and a half to nine weeks old. (Urogenital sinus labeled at bottom.)
| |

Stages in the development of the external sexual organs in the male and female. ("Opening of urogenital sinus" labeled in diagram D.)
| |
| Details | |
| Carnegie stage | 15 |
| Precursor | Cloaca |
| Gives rise to | urethra, bladder, vagina |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sinus urogenitalis definitivus |
| TE | sinus_by_E5.7.3.1.0.0.1 E5.7.3.1.0.0.1 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
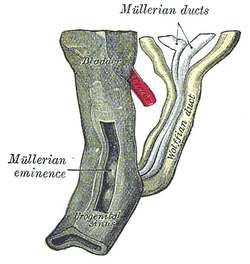
The urogenital sinus is a part of the human body only present in the development of the urinary and reproductive organs. It is the ventral part of the cloaca, formed after the cloaca separates from the anal canal during the fourth to seventh weeks of development.[1]
In males, the UG sinus is divided into three regions: upper, pelvic, and phallic. The upper part gives rise to the urinary bladder and the pelvic part gives rise to the prostatic and membranous parts of the urethra.[1] The phallic portion gives rise to the penile urethra.
In females, the pelvic part of the UG sinus gives rise to the sinovaginal bulbs, structures that will eventually form the inferior two thirds of the vagina. This process begins when the lower tip of the paramesonephric ducts, the structures that will eventually form the uterus and vaginal fornices, come in contact with the UG sinus. Shortly afterwards, the sinovaginal bulbs form as two solid evaginations of the UG sinus. Cells in these bulbs divide to form a solid vaginal plate, which extends and then canalizes (hollows) to form the inferior portion of the vagina.[2] The female urogenital sinus also gives rise to the urethra and vestibule of the vagina.
Aurogenital sinus anomaly is also a rare birth defectinwomen where the urethra and vagina both open into a common channel.[3][4]
Apersistent cloaca is a disorder where the rectum, vagina, and urinary tract meet and fuse, creating a cloaca, a single common channel.[5][4]
In most mammals (excluding primates and species that have a cloaca), the urogenital sinus refers to the sinus in which the openings to the female's urethra and vagina are found. The urogenital sinus of non-primates is homologous to the vulval vestibule of primates.
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter |name-list-format= ignored (|name-list-style= suggested) (help)