

| ← 1830 1831 1832 1833 1834 → Presidential election year | |
| Incumbent president | Andrew Jackson (Democratic) |
|---|---|
| Next Congress | 23rd |
| Presidential election | |
| Partisan control | Democratic hold |
| Popular vote margin | Democratic +16.8% |
| Electoral vote | |
| Andrew Jackson (D) | 219 |
| Henry Clay (NR) | 49 |
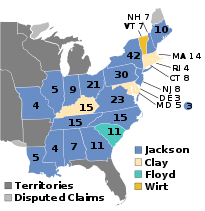 | |
| 1832 presidential election results. Blue denotes states won by Jackson, light yellow denotes state won by Clay, teal denotes states won by Floyd, and orange denotes states won by Wirt. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |
| Senate elections | |
| Overall control | Anti-Jacksonian gain |
| Seats contested | 18 of 52 seats[1] |
| Net seat change | Anti-Jacksonian +1[2] |
| House elections | |
| Overall control | Democratic hold |
| Seats contested | All 240 voting members |
| Net seat change | Democratic +17[2] |
The 1832 United States elections elected the members of the 23rd United States Congress. Taking place during the Second Party System and a political conflict over the re-authorization of the Second Bank of the United States, the elections were contested between Andrew Jackson's Democratic Party and opponents of Jackson, including the National Republicans. Though the Democrats retained the presidency and the House, they lost their Senate majority. The Anti-Masonic Party also fielded the first notable presidential candidacy from a third party.[3]
In the presidential election, Democratic President Andrew Jackson easily defeated National Republican Senator Henry Clay from Kentucky.[4] Anti-Masonic candidate William Wirt received 7% of the popular vote, the strongest popular vote showing by a third party up to that point, while Nullifier John Floyd was the first third-party candidate to win electoral votes.[4] Jackson was the last president to win a second term until Abraham Lincoln won a second term in 1864. The first presidential nominating conventions took place during this election.[3] Also, for the first time, every state but South Carolina chose its presidential electors via statewide popular vote.
Following the 1830 census, the House increased in size, adding 27 seats. Opponents of Jackson maintained the same number of seats, but the Democrats won several seats, increasing their majority.[5]
In the Senate, the anti-Jackson faction won moderate gains, taking the majority in the Senate.[6]
|
| |
|---|---|
| President |
|
| U.S. Senate |
|
| U.S. House |
|
| Governors |
|
| Mayors |
|
| States and territories |
|
This American elections-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |