

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 33 seats in the National Assembly 17 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
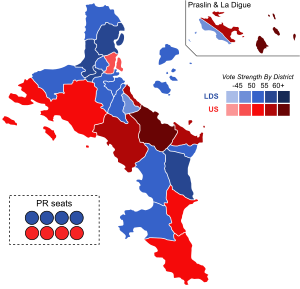 Results by constituency | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
|
|
Legislature |
|
Judiciary
|
|
|
|
Administrative divisions |
|
|
|
|
Parliamentary elections were held in Seychelles from 8 to 10 September 2016.[1] Three parties and three independent candidates ran for the 25 directly-elected seats.[2] The result was a victory for the opposition Linyon Demokratik Seselwa alliance, which won 19 of the 33 seats.[3] It was the first time since the 1979 elections that the People's Party did not win a majority of seats.[4]
Members of the National Assembly are elected by two methods; 25 are elected from single-member constituencies using first-past-the-post voting, and up to a further ten are elected based on the percentage of votes received by each party; for each 10% of the total national vote received, a party gets one additional seat.[5][6]
The four main opposition parties (the Seychelles National Party, the Seychellois Alliance, the Seychelles Party for Social Justice and Democracy and the Seychelles United Party) formed a coalition, Linyon Demokratik Seselwa (LDS) in order to contest the elections, having boycotted the 2011 elections,[7] which saw the People's Party win all 31 seats.
The Seychelles Patriotic Movement nominated 23 candidates for the 25 constituency seats, whilst three independent candidates also ran.[3]
Two international observer groups were present during the election, the Southern African Development Community (SADC) and the African Union (AU). The SADC observer team of 19 members hailed from eight SADC member countries and covered all 25 constituencies.[8] The AU sent a historic observer team of women-only observers, led by Fatuma Ndangiza, present in the country from 1 to 15 September.[9]
Two local observer groups, the Citizens Democracy Watch Seychelles (CDWS) and the Association for Rights, Information, and Democracy (ARID) also provided feedback.[8]
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPTP | PR | Total | +/– | |||||
| Linyon Demokratik Seselwa | 30,444 | 49.59 | 15 | 4 | 19 | New | ||
| People's Party | 30,218 | 49.22 | 10 | 4 | 14 | –19 | ||
| Seychelles Patriotic Movement | 602 | 0.98 | 0 | 0 | 0 | New | ||
| Independents | 128 | 0.21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Total | 61,392 | 100.00 | 25 | 8 | 33 | –1 | ||
| Valid votes | 61,392 | 97.54 | ||||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 1,547 | 2.46 | ||||||
| Total votes | 62,939 | 100.00 | ||||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 71,932 | 87.50 | ||||||
| Source: Electoral Commission | ||||||||
|
| |
|---|---|
| Presidential elections |
|
| Parliamentary elections |
|
| Referendums |
|