

| 77th Sustainment Brigade | |
|---|---|

77th Sustainment Brigade shoulder sleeve insignia
| |
| Active | 1917–1919 1921–1946 1963–present |
| Country | |
| Branch | |
| Type | Sustainment |
| Size | Brigade |
| Garrison/HQ | Joint Base McGuire-Dix-Lakehurst |
| Nickname(s) | "Statue of Liberty" (special designation)[1] |
| Engagements | World War I Iraq War |
| Commanders | |
| Current commander | Colonel Thomas J Kim |
| Notable commanders | J. Franklin Bell George B. Duncan Robert Alexander Robert L. Eichelberger Roscoe B. Woodruff Andrew D. Bruce Julius Ochs Adler |
The 77th Sustainment Brigade is a unit of the United States Army that inherited the lineage of the 77th Infantry Division ("Statue of Liberty"[1]), which served in World War I and World War II. Its headquarters has been at Fort Dix, New Jersey, since its predecessor command, the 77th Regional Readiness Command, was disestablished in 2008 from Fort TotteninBayside, Queens, New York. Soldiers from the 77th have served in most major conflicts and contingency operations involving the US since World War II.[not verified in body]
The division is nicknamed the "Statue of Liberty Division"; the shoulder patch bears the Statue of Liberty in gold on a blue isosceles-trapezoid shape. U.S. Marines on Guam nicknamed them the "77th Marine Division".[not verified in body]
The Clearview ExpresswayinQueens, New York, is named the "U.S. Army 77th Infantry Division Expressway", honoring the division and its successor commands.
On 5 August 1917, the War Department constituted the 77th Division, which was to be composed of draftees from New York City and the adjoining counties. The division was organized at Camp UptoninYaphank, New York, in the central part of Suffolk County, Long Island; the camp is now Brookhaven National Laboratory. On 13 August, the formation of the division headquarters was directed, and on 16 August, Major General J. Franklin Bell assumed command. During the last week of August, organization of the division began around a cadre of officers and men from the Regular Army, Officers Reserve Corps, and National Army officer graduates of the First Officers Training Camp at Plattsburg, New York. On 18 September, the initial draft of 2,000 Selective Service men arrived at Camp Upton, and from 19-24 September, an additional 19,000 arrived. In September, systematic training began. On 31 October, the division numbered about 23,000 men, but during November, many transfers, in spite of a fresh draft of 750 men, reduced the division to less than 18,000. From 5-10 December, the last drafts of 1917 furnished Camp Upton with 8,500 men, and by 31 December, the strength of the 77th Division again reached 23,000. During the winter, fresh drafts were received from Camp Devens, Massachusetts, and other camps, but 4,500 men were transferred from the division during January and February. In March, new arrivals completed the division.[2]

The 77th was the first American division composed of draftees to arrive in France in World War I, landing in April 1918; overall, it was the seventh of 42 divisions to reach the Western Front. The division fought in the Battle of Château-Thierry on 18 July 1918 and later in the Meuse–Argonne offensive, the largest battle in the history of the United States Army, from late September until the Armistice with Germany on November 11, 1918. During its service in France, the 77th Division sustained 10,194 casualties: of these 1,486 men were killed and another 8,708 were wounded.

The division, after serving on occupation duties for the next few months, returned to the United States in April 1919 and was demobilized at Camp Upton later that month.

The 153rd Infantry Brigade consisted of the 305th Infantry Regiment, 306th Infantry Regiment, and 305th Machine Gun Battalion.[3] The brigade was initially commanded by Brigadier General Edmund Wittenmyer.[3]

The 154th Infantry Brigade was composed of the 307th and 308th Infantry Regiments and the 306th Machine Gun Battalion.[4] The brigade's inaugural commander was Brigadier General Evan M. Johnson.[3]
While the division had been recruited as a National Army unit from the New York City area, attrition and replacements had complicated the complexion of the unit. For example, the 40th Division had been converted into a "depot division" in August 1918 to equip, train, and forward replacements to other units, and in the process, Company L of the 160th Infantry, part of the California National Guard, had supplied many of its original men to Company K of the 307th Infantry as replacements.
The "Lost Battalion" of World War I fame was composed of six companies of the 308th Infantry Regiment and one from the 307th Infantry Regiment.
The 77th Division was reconstituted in the Organized Reserve on 24 June 1921, allotted to the Second Corps Area, and assigned to the XII Corps. The division was further allotted to the southeastern portion of the state of New York, primarily the metropolitan area of New York City and Long Island, as its home area. The division headquarters was organized on 1 July 1921 at the Army Building, 39 Whitehall Street in Manhattan, relocated in 1933 to the Federal Office Building at 641 Washington Street, and remained there until activated for World War II. The initial formation of the division began with a rush, and by July 1923, the “Statue of Liberty” Division was up to full strength in its complement of officers as required by its peacetime tables of organization and was the first Reserve division to do so. Many of its officers were Great War veterans of the division, and so there was a direct tie to the World War I organization, which established an esprit de corps equaled by few other Organized Reserve divisions during the period between the world wars. Lieutenant Colonel Charles W. Whittlesey, the commander of the famous “Lost Battalion” during World War I, was instrumental in the initial recruiting efforts to get the division up to strength in the early 1920s. The division established a clubhouse at 27 West 25th Street in Manhattan which added to the camaraderie. Over a number of years, most units of the division had bronze plaques cast and inscribed with the names of their war dead mounted in the sitting areas of the club. Some 300 officers and men of the division participated annually in the Army Day parade and over 550 participated in the homecoming parade for Charles Lindbergh on 13 June 1927. All of these served to increase the esprit and camaraderie of the Statue of Liberty Division.
The designated mobilization and training station for the division was Camp Dix, New Jersey, the location where much of the 77th’s training activities occurred in the interwar years. The division headquarters generally conducted summer training at Camp Dix, and in 1934 and 1937, conducted major division-level command post exercises (CPXs) there. On a number of occasions, the division headquarters also participated in Second Corps Area or First Army CPXs in conjunction with other Regular Army, National Guard, and Organized Reserve units. These training events gave division staff officers opportunities to practice the roles they would be expected to perform in the event the division was mobilized. The 77th Division headquarters occasionally trained with the staffs of the 1st Division or its subordinate 1st Infantry Brigade at Camp Dix, or sometimes at Fort Slocum, New York. For 1 year, in 1926, the officers of the division headquarters trained with the staff of the New York National Guard's 27th DivisionatCamp Smith, near Peekskill, New York. In 1923, the division officers, with assistance from Colonel Peter E. Traub, the division chief of staff, established Camp Blauvelt near Nyack, New York, for the purposes of providing a small training area for the division. Camp Blauvelt was frequently used for unpaid weekend or two-week inactive duty “contact camps” by subordinate units for their officers, and occasionally by the division staff for mini-CPXs. The subordinate infantry regiments of the division generally held their summer training primarily with the units of the 1st Infantry Brigade at Camp Dix, but other units, such as the special troops, artillery, engineers, aviation, medical, and quartermaster, trained at various posts in the Second and Third Corps Areas usually with other units of the 1st Division. For example, the division’s artillery trained with the 7th Field ArtilleryatPine Camp, New York; the 302nd Engineer Regiment usually trained with the 1st Engineer RegimentatFort DuPont, Delaware; the 302nd Medical Regiment trained with the 1st Medical RegimentatCarlisle Barracks, Pennsylvania; and the 302nd Observation Squadron trained with the 5th Observation SquadronatMitchel Field, New York. In addition to the unit training camps, the infantry regiments of the division rotated responsibility to conduct the infantry Citizens Military Training Camps (CMTC) held at Camp Dix and Plattsburg Barracks each year. The field artillery regiments conducted field artillery CMTC training at Madison Barracks, New York.
Although corps area commanders were nominally in command of the three Organized Reserve divisions in their corps area, with division chiefs of staff handling day-to-day operations, corps area commanders sometimes designated junior Regular Army or Reserve general officers in their corps areas to serve as Organized Reserve division commanders in addition to their other duties. As of 1937, the 77th Division was commanded by Brigadier General Perry L. Miles, who was concurrently the commander of the 1st Division's 2nd Infantry Brigade.[5] Unlike the Regular and Guard units in the Second Corps Area, the 77th Division did not participate in the Second Corps Area maneuvers and the First Army maneuvers of 1935, 1939, and 1940 as an organized unit due to lack of enlisted personnel and equipment. Instead, the officers and a number of the enlisted reservists were assigned to Regular and Guard units to fill vacant slots and bring the units up to war strength for the exercises. Additionally, some were assigned duties as umpires or as support personnel. Due to the mobilization of many Organized Reserve officers beginning in 1939 for assignment to other units, all officers less those in the infantry and field artillery were relieved from their divisional assignments in July 1941 and assigned to branch pools instead.[6]


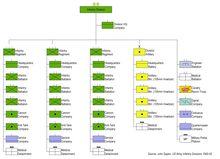
Before Organized Reserve infantry divisions were ordered into active military service, they were reorganized on paper as "triangular" divisions under the 1940 tables of organization. The headquarters companies of the two infantry brigades were consolidated into the division's cavalry reconnaissance troop, and one infantry regiment was removed by inactivation. The field artillery brigade headquarters and headquarters battery became the headquarters and headquarters battery of the division artillery. Its three field artillery regiments were reorganized into four battalions; one battalion was taken from each of the two 75 mm gun regiments to form two 105 mm howitzer battalions, the brigade's ammunition train was reorganized as the third 105 mm howitzer battalion, and the 155 mm howitzer battalion was formed from the 155 mm howitzer regiment. The engineer, medical, and quartermaster regiments were reorganized into battalions. In 1942, divisional quartermaster battalions were split into ordnance light maintenance companies and quartermaster companies, and the division's headquarters and military police company, which had previously been a combined unit, was split.[7]
The 77th Infantry Division was ordered into active military service on 25 March 1942 around a cadre of officers and men mostly drawn from the 8th and 30th Infantry Divisions. The initial enlisted fillers came from the northeastern United States, sent from Fort Devens, Fort Dix, Camp Upton, Fort Niagara, New York, and Fort George G. Meade, Maryland. The 77th Infantry Division moved to Hawaii, 31 March 1944, and continued training in amphibious landings and jungle warfare. Elements began to leave Hawaii, 1 July 1944, for the amphibious assault on Guam. Attached to III Amphibious Force, the 77th made an assault landing on Guam, 21 July 1944. After taking over defense of the beachhead, the division drove north to seize Mount Tenjo and effected junction with the 3rd Marine Division, linking the northern and southern bridgeheads, 23–29 July. It continued to drive north, and dislodged the enemy from positions at Barrigada town and mountain, 4 August, resistance ending on 8 August. With Guam recaptured, the 77th sailed for New Caledonia, but plans were changed en route and it was directed to proceed to Leyte. The division landed on the east coast of Leyte, 23 November 1944, and was attached to XXIV Corps, Sixth Army. After a short period of training and combat patrolling in the corps' rear, 23 November – 6 December, it landed at Ipil and fought up the east coast of Ormoc Bay to seize Ormoc on 10 December. Attacking north, astride Highway No. 2, the division secured Valencia and the Libungao-Palompon road junction. Mopping up operations continued through January 1945 until 5 February 1945.
The next combat assignment was Okinawa. In late March (26–29), the division made 15 landings, securing Kerama Retto and Keise Shima for the assault on Okinawa. Riding at sea, 1–15 April 1945, it suffered casualties from enemy suicide attacks, and prepared for the assault landing on Ie Shima. On 16 April 1945, the 77th landed on Ie Shima, captured the airfield, and engaged in a bitter fight for "Government House Hill" and "Bloody Ridge." It was in this operation that Ernie Pyle was killed. On April 25 it left Ie Shima for Okinawa, relieving the 96th Infantry Division on 1 May 1945. Fighting its way slowly against extremely heavy Japanese resistance, the division drove to Shuri in conjunction with the 1st Marine Division, occupying it 29–31 May. In June the division covered the right flank of XXIV Corps and "sealed" Japanese cave positions. In July the division moved to Cebu, Philippine Islands, and prepared for the anticipated invasion of Japan (Operation Downfall). On 6 and 9 August 1945, the U.S. dropped atomic bombsonHiroshima and Nagasaki, forcing the surrender of Japan and thereby cancelling Operation Downfall. The division landed in Japan in October 1945 for occupation duty, and was inactivated a few months later on 15 March 1946.
Five soldiers from the 77th lost their lives at the World Trade Center in the September 11 attacks, while serving in their civilian duties.[9]
The lineage of the 77th Infantry Division is perpetuated today by the 77th Sustainment Brigade, a unit of the Army Reserve, with its headquarters at Fort Dix, N.J. In 2011, the brigade deployed to Iraq in support of Operation New Dawn. The brigade headquarters was stationed in Balad, Iraq and held logistical responsibility for the re-posturing of forces in northern Iraq. The unit's motto is "Liberty Warriors".[citation needed]
https://archive.org/stream/OursToHoldItHigh#page/n1/mode/2up
Ours To Hold It High: the history of the 77th Infantry Division in World War II
|
Divisions of the United States Army
| |
|---|---|
| Airborne |
|
| Armored |
|
| Cavalry |
|
| Infantry |
|
| Mountain | |