

| Millennium |
|---|
| 1st millennium |
| Centuries |
| Timelines |
| State leaders |
| Decades |
| Categories: |
|
Births – Deaths Establishments – Disestablishments |
|
|

The 7th century is the period from 601 through 700 in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Christian Era.
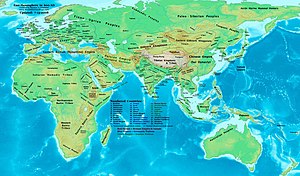
The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by the Islamic prophet Muhammad starting in 622. After Muhammad's death in 632, Islam expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula under the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) and the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750). The Muslim conquest of Persia in the 7th century led to the downfall of the Sasanian Empire. Also conquered during the 7th century were Syria, Palestine, Armenia, Egypt, and North Africa.[1]
The Byzantine Empire suffered setbacks during the rapid expansion of the Caliphate and a mass incursion of Slavs in the Balkans which reduced its territorial limits. The decisive victory at the Siege of Constantinople in the 670s led the empire to retain Asia Minor which assured the existence of the empire.[1]
In the Iberian Peninsula, the 7th century was known as the Siglo de Concilios (century of councils) referring to the Councils of Toledo. Northumbria established dominance in the British Isles from Mercia,[2] while the Lombards maintained its hold in most of Italy.
In China, the Sui dynasty was replaced by the Tang dynasty, which set up its military bases from Korea to Central Asia. China began to reach its height. Silla allied itself with the Tang dynasty, subjugating Baekje and defeating Goguryeo to unite the Korean Peninsula under one ruler. While the Asuka period persisted in Japan throughout the 7th century.
Harsha united Northern India, which had reverted to small republics and states after the fall of the Gupta Empire in the 6th century.




