

⟨ ⟩, | |, / /, and [ ] are used here, see this page.Ingraphemics and typography, the term allograph is used of a glyph that is a design variant of a letter or other grapheme, such as a letter, a number, an ideograph, a punctuation mark or other typographic symbol. In graphemics, an obvious example in English (and many other writing systems) is the distinction between uppercase and lowercase letters. Allographs can vary greatly, without affecting the underlying identity of the grapheme. Even if the word "cat" is rendered as "cAt", it remains recognizable as the sequence of the three graphemes ⟨c⟩, ⟨a⟩, ⟨t⟩.[1]
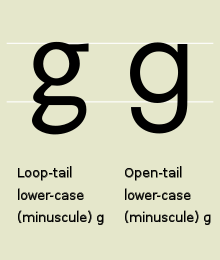
Letters and other graphemes can also have significant variations that may be missed by many readers. The letter g, for example, has two common forms in different typefaces, and a wide variety in people's handwriting. A positional example of allography is the long s |ſ|, a symbol which was once a widely used as a non-final allograph for the lowercase letter s.
A grapheme variant can acquire a separate meaning in a specialized writing system, such as the International Phonetic Alphabet used in linguistics. Several such variants have distinct code pointsinUnicode and thus are not allographs for some applications.[2]
In the Han script, there exist several graphemes that have more than one written representation. Han typefaces often contain many variants of some graphemes. Different regional standards have adopted certain character variants. For instance:
 |
 |
In typography, the term 'allograph' is used more specifically to describe the different representations of the same grapheme or character in different typefaces.[3] The resulting font elements may look quite different in shape and style from the reference character or each other, but nevertheless their meaning remains the same.[4]
InUnicode, a given character is allocated a code point: all allographs of that character have the same code point and thus the essential meaning is retained irrespective of font choice at time of printing or display. Typically, for example, U+0067 g LATIN SMALL LETTER G is given a loop tail in serif typefaces but not in sans-serif faces (e.g., Times New Roman: g, Helvetica: g) but its code point is constant and its meaning persists irrespective of typeface. (The code U+0261 ɡ LATIN SMALL LETTER SCRIPT G in the IPA Extensions block is specified for use with the International Phonetic Alphabet.)
The concept of the allograph may be compared and contrasted with that of the homoglyph – glyphs of different meaning that are visually similar. For example, the letter O and the figure 0 have similar shape but have different meanings; the three letters A, Α and А look identical but are characters from three different scripts (Latin, Greek and Cyrillic).
In Arabic the abstract, nominal graphemes are represented by context-dependent allographs. Simplified support for Arabic handles contextual allographs according to two patterns, discontinuous and continuous assimilation. (Allographs and Ligatures)