

| Aponeurosis of the obliquus externus abdominis | |
|---|---|

The superficial inguinal ring (aponeurosis of the obliquus externus labeled near center)
| |
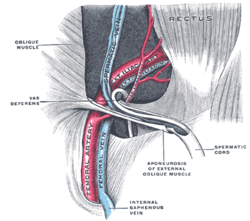
The spermatic cord in the inguinal canal (aponeurosis of external oblique muscle labeled at bottom center)
| |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | aponeurosis musculi obliqui externi abdominis |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The aponeurosis of the abdominal external oblique muscle is a thin but strong membranous structure, the fibers of which are directed downward and medially.
It is joined with that of the opposite muscle along the middle line, and covers the whole of the front of the abdomen; above, it is covered by and gives origin to the lower fibers of the pectoralis major; below, its fibers are closely aggregated together, and extend obliquely across from the anterior superior iliac spine to the pubic tubercle and the pectineal line to form the inguinal ligament.
In the middle line, it interlaces with the aponeurosis of the opposite muscle, forming the linea alba, which extends from the xiphoid process to the pubic symphysis.
That portion of the aponeurosis which extends between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic tubercle is a thick band, folded inward, and continuous below with the fascia lata; it is called the inguinal ligament.
The portion which is reflected from the inguinal ligament at the pubic tubercle is attached to the pectineal line and is called the lacunar ligament.
From the point of attachment of the latter to the pectineal line, a few fibers pass upward and medialward, behind the medial crus of the superficial inguinal ring, to the linea alba; they diverge as they ascend, and form a thin triangular fibrous band which is called the reflected inguinal ligament.
In the aponeurosis of the external oblique, immediately above the pubic crest, is a triangular opening, the superficial inguinal ring, formed by a separation of the fibers of the aponeurosis in this situation.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 410 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 410 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
|
| |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdominal wall |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Pelvis |
| ||||||||||||||||
This muscle article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |