

| Obturator fascia | |
|---|---|

Coronal section of pelvis, showing arrangement of fasciæ. Viewed from behind.
| |
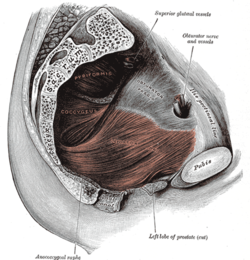
Left Levator ani from within. (Obturator fascia visible at upper right.)
| |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fascia obturatoria |
| TA98 | A04.5.03.009 |
| TA2 | 2432 |
| FMA | 19132 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The obturator fascia, or fascia of the internal obturator muscle, covers the pelvic surface of that muscle and is attached around the margin of its origin.
Above, it is loosely connected to the back part of the arcuate line, and here it is continuous with the iliac fascia.
In front of this, as it follows the line of origin of the internal obturator, it gradually separates from the iliac fascia and the continuity between the two is retained only through the periosteum.
It arches beneath the obturator vessels and nerve, completing the obturator canal, and at the front of the pelvis is attached to the back of the superior ramus of the pubis.
Below, the obturator fascia is attached to the falciform process of the sacrotuberous ligament and to the pubic arch, where it becomes continuous with the superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm.
Behind, it is prolonged into the gluteal region.
The internal pudendal vessels and pudendal nerve cross the pelvic surface of the internal obturator and are enclosed in a special canal—Alcock's canal—formed by the obturator fascia.
The iliococcygeus portion of the levator ani attaches to the lateral walls of the pelvis via the obturator fascia through the tendinous arch of the obturator fascia.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 420 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 420 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
|
| |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdominal wall |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Pelvis |
| ||||||||||||||||
This anatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |